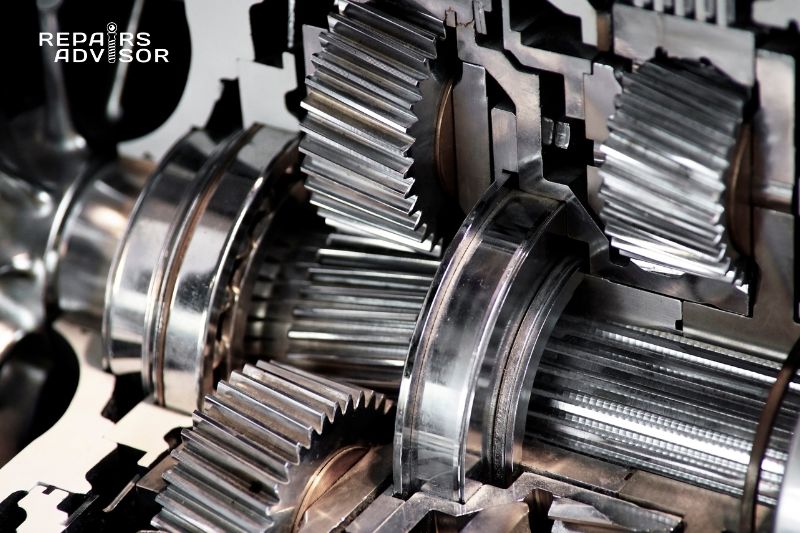
Did you know that no one component in your car has more going on inside it than your transmission?
Modern vehicle transmissions use a combination of sophisticated hydraulics and computer-controlled electronic components to transfer engine power to the driveshaft and wheels, and most modern drivers remain blissfully unaware of these complex systems until something goes awry.
Without a doubt, your vehicle’s transmission is the most complicated and least understood system in your car or truck, so it is little wonder that the majority of car questions, and repair service calls have to do with transmission systems.
Have you ever wondered what kind of transmission your car or truck has under the hood? If so, you’re either in need of a repair due to transmission problems, such as high engine revs and transmission slipping, or you’re just curious about what goes on under the hood. In either case, Repairs Advisor is here to help!
Quick Identification Methods
Using Your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Your VIN is like your vehicle’s fingerprint, containing detailed information about your transmission. Located on your dashboard near the windshield (driver’s side), door jamb, or engine block, this 17-character code holds the key to quick identification.
The eighth character in your VIN typically indicates engine type, while positions 4-8 together often reveal transmission information. However, VIN decoding varies by manufacturer and model year, making online VIN decoder tools invaluable. Popular free decoders include the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) database and manufacturer-specific websites.
For comprehensive vehicle specifications including detailed transmission information, consider accessing our vehicle manual collections which provide manufacturer-sourced documentation for accurate identification.
Limitations to Consider:
- Some older vehicles (pre-1981) may have non-standard VINs
- Aftermarket transmission swaps won’t reflect in VIN data
- Rebuilt transmissions may retain original VIN information despite internal changes
Checking Your Owner’s Manual and Documentation
Your owner’s manual contains transmission specifications in the “Specifications” or “Fluids and Capacities” sections. Look for terms like “automatic transmission,” “manual transmission,” or specific model designations (e.g., “6-speed automatic 6R80”).
For vehicles missing original documentation, digital manuals offer excellent alternatives. Many manufacturers provide online access to owner’s manuals, while aftermarket sources offer comprehensive repair documentation for older or specialty vehicles.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Safety First: Before any under-hood inspection, ensure your engine is cool, parking brake is engaged, and you’re working on level ground.
Transmissions are typically located between the engine and drive wheels. Automatic transmissions appear larger and more complex, with fluid dipsticks, cooler lines, and electrical connections. Manual transmissions look simpler, connecting directly to a clutch assembly without the bulky torque converter housing characteristic of automatics.
What Transmission Do I Have: Types of transmission
There are many types of transmissions, including automatic, manual, continuously variable, dual clutch, and automated manual.
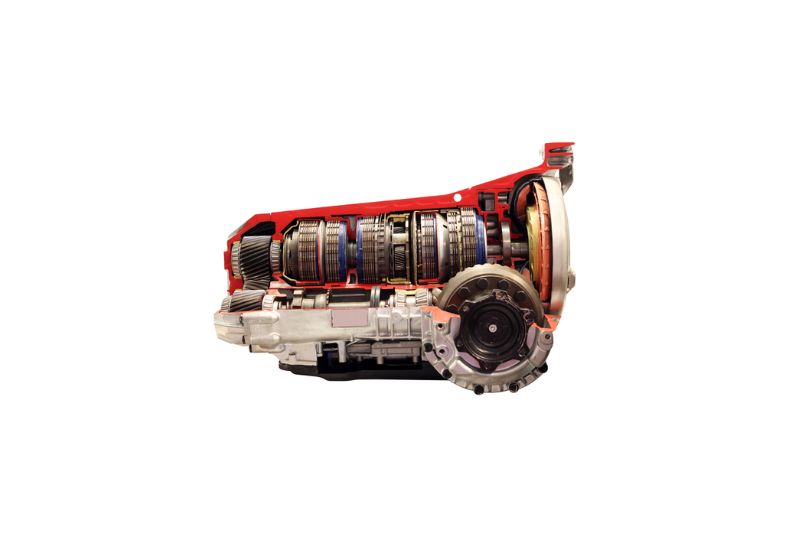
Automatic transmission
An automatic transmission is a system in a car that changes gears automatically based on driving conditions. It allows drivers to focus on driving instead of shifting gears manually.
- The most common transmission for passenger cars and light trucks
- Uses a fluid coupling to transmit power from the engine to the wheels
- Shifts gears automatically, making it easier to use than a manual transmission
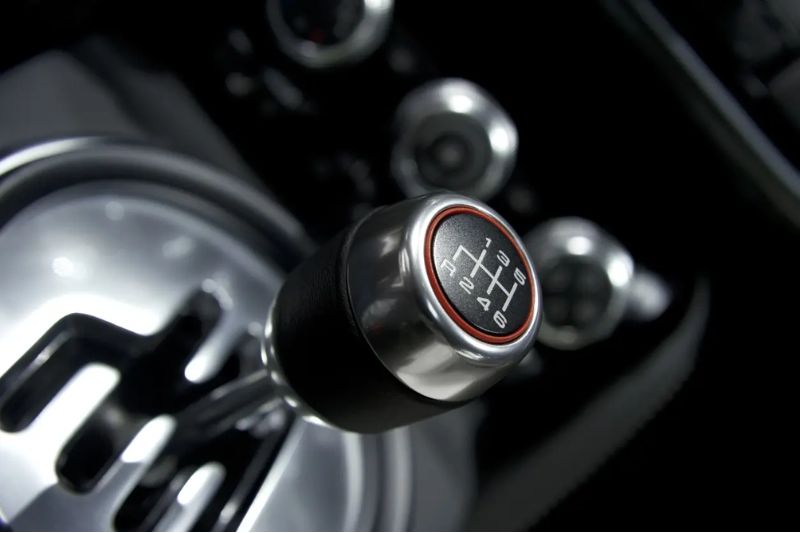
Manual transmission
A manual transmission is a transmission that requires a driver to use a clutch pedal and gear shifter to change gears. It’s also known as a standard transmission or stick shift.
- Also known as a stick shift or standard transmission
- The driver manually selects and engages gears using a gear shifter and clutch pedal
- Offers a sense of control that automatics can’t match

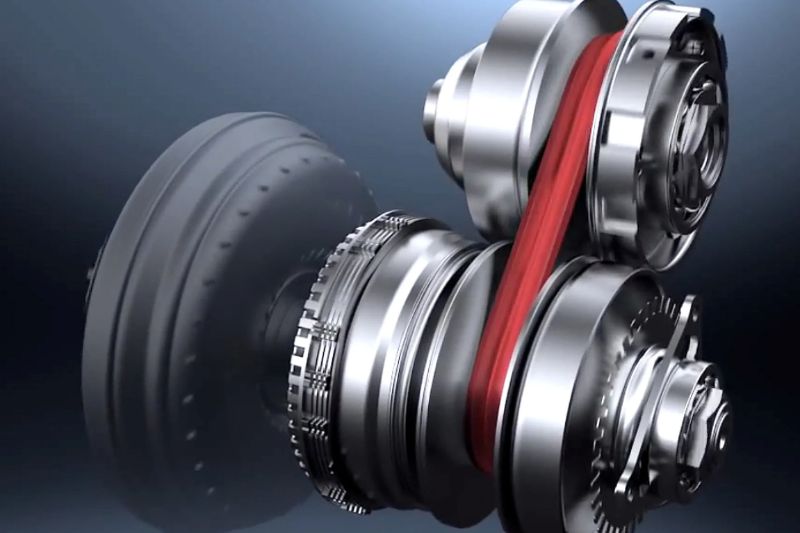
Continuously variable transmission (CVT)
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automatic transmission that can smoothly change gear ratios. CVTs are also known as shiftless, stepless, or single-speed transmissions.
- A newer and increasingly popular type of transmission
- Uses a system of belts and pulleys to continuously vary the transmission ratio
- Allows for a seamless, stepless acceleration and improved fuel efficiency

Dual clutch transmission
A dual clutch transmission (DCT) is a type of transmission that uses two clutches to automatically shift gears. It combines the efficiency of a manual transmission with the convenience of an automatic transmission.
- A “hybrid” between an automatic and a manual transmission
- Uses two clutches and can switch gears faster than a manual or automatic transmission

Automated manual transmission (AMT)
An automated manual transmission (AMT) is a type of transmission that combines manual and automatic features. It’s similar to a manual transmission, but uses a computer to shift gears and operate the clutch.
- Combines the benefits of manual and automatic transmissions
- The driver can still shift gears manually, but the car will automatically shift gears for you if you choose to let it

You can also watch this video to learn more about different types of transmission systems:
Manual vs. Automatic Transmission Identification
Manual Transmission Characteristics
The most obvious indicator is a clutch pedal—if your vehicle has three pedals, you have a manual transmission. The gear shifter typically shows a pattern (like an “H” shape) with numbered positions and sometimes reverse indicated separately.
Under the hood, manual transmissions appear more compact and connect directly to the engine via a clutch assembly. They lack the fluid dipstick and cooling lines common to automatic transmissions. Popular manual transmission types include 5-speed and 6-speed configurations, with some performance vehicles offering 7-speed options.
Manual transmissions require specific gear oil rather than automatic transmission fluid (ATF), making proper identification crucial for maintenance. For detailed manual transmission repair procedures, explore our drivetrain system guides which cover clutch, transmission, and related component maintenance.
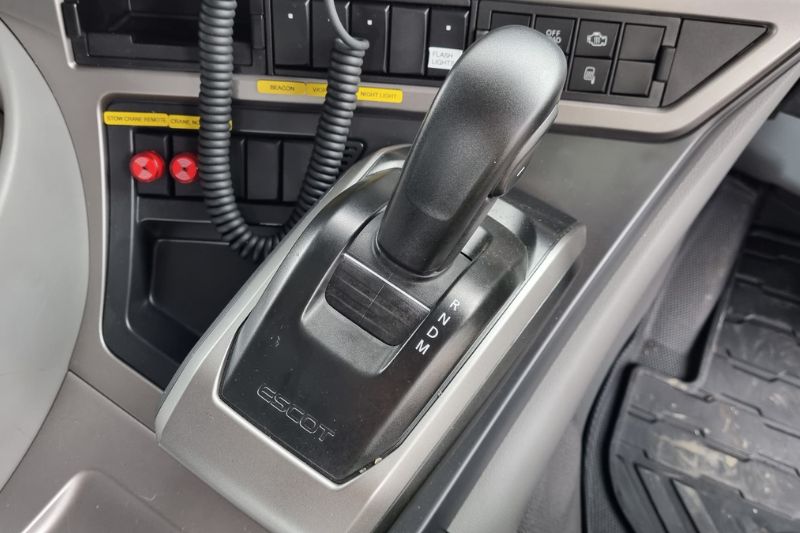
Automatic Transmission Characteristics
Automatic transmissions feature the familiar PRNDL (Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, Low) gear selector pattern, though modern vehicles may have additional positions like Sport or Manual modes.
Key identifying features include:
- ATF dipstick (usually red or yellow handle)
- Transmission cooler lines running to the radiator
- Larger, more complex case design
- Torque converter housing (large circular section at engine connection)
- Multiple electrical connections for solenoids and sensors
CVT Recognition: Continuously Variable Transmissions lack traditional gear ratios, offering smooth acceleration without gear shifts. CVTs often have unique fluid requirements and may display “CVT” markings on the case or dipstick.
Physical Identification Methods
Transmission Pan Shape and Bolt Patterns
The oil pan underneath your transmission provides one of the most reliable identification methods. Different transmission families use distinct pan shapes and bolt patterns that serve as identification fingerprints.
Common pan shapes include:
- Rectangular with rounded corners: Often found on Ford and GM 4-speed automatics
- Irregular polygon shapes: Typical of modern 6+ speed transmissions
- Deep, complex shapes: Common on newer transmissions with integrated filters
Count the bolt holes around the pan perimeter—this number often indicates transmission type. For example, many Ford 4R70W transmissions use 20-bolt pans, while GM 4L60E transmissions typically have 16 bolts.
Pro Tip: Take a photo of your pan shape and bolt pattern for comparison with online identification guides or when consulting with parts suppliers.
Transmission Case Markings and Numbers
Manufacturers stamp identification numbers directly onto transmission cases, usually on flat surfaces near the bell housing or on dedicated tags. These markings include:
- Part numbers: Long alphanumeric codes identifying specific transmission models
- Serial numbers: Individual transmission identification for warranty and service tracking
- Date codes: Manufacturing date information
- Build information: Assembly plant and specification details
Clean the area with degreaser and a wire brush to reveal worn markings. Use a flashlight or phone light to illuminate recessed numbers. Common locations include the driver’s side case surface, bell housing flange, or dedicated identification tags.
Cross-reference these numbers with manufacturer databases or aftermarket identification guides. Many brand-specific manual collections include transmission identification charts for accurate cross-referencing.
Fluid Type and Color Identification
Transmission fluid characteristics provide valuable identification clues. Check the dipstick (if equipped) or fluid during service for these indicators:
Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF):
- Typically red, pink, or amber when new
- Sweet or mild petroleum odor
- Flows easily at room temperature
- May be specified as Dexron, Mercon, or manufacturer-specific formulations
Manual Transmission Fluid:
- Often heavier gear oil (75W-90, 80W-90)
- May be regular ATF in some applications
- Darker amber or black color
- Thicker consistency than ATF
Warning Signs: Dark brown or black fluid with burnt odors indicates transmission problems requiring immediate attention. Never use the wrong fluid type, as this can cause severe damage within miles of operation.
Brand-Specific Identification Guides
Ford Transmission Identification
Ford uses alphanumeric codes stamped on the case or displayed on identification tags. Popular Ford automatic transmissions include:
- 4R70W: 4-speed automatic, common in trucks and SUVs (1993-2008)
- 6R80: 6-speed automatic, found in F-150s and Mustangs (2009+)
- 10R80: 10-speed automatic, latest generation F-150s and Mustangs (2017+)
Ford manual transmissions include the T5, T45, TR3650, and MT82 series. The identification tag is typically located on the left side of the case, visible from above.
For comprehensive Ford transmission specifications and repair procedures, our FORD Manuals collection provides detailed factory documentation including identification charts and service procedures.
GM/Chevrolet Transmission Identification
General Motors uses a combination of case stampings and identification tags. Common GM automatic transmissions include:
- 4L60E: Electronic 4-speed, widely used in trucks and SUVs (1992-2013)
- 6L80E: 6-speed automatic, found in trucks and performance cars (2006+)
- 8L90E: 8-speed automatic, latest Corvettes and Camaros (2015+)
GM identification numbers are typically stamped on the right rear of the case, visible from underneath. The format usually includes letters indicating transmission family followed by numbers for specific variants.
Manual transmissions include the NV3500, NV4500, and T56 series, with identification tags on the side case surfaces.
Chrysler/Dodge/Jeep Transmission Identification
Chrysler Corporation (now Stellantis) uses various identification methods depending on the era. Common automatic transmissions include:
- 42RLE: 4-speed automatic, Jeep Wrangler and Cherokee applications
- 68RFE: 6-speed automatic, Ram trucks and heavy-duty applications
- 8HP70: 8-speed automatic, modern Charger, Challenger, and Jeep applications
Chrysler identification tags are often located on the left side of the case or stamped into the bell housing area. Look for alphanumeric codes beginning with numbers followed by letters (e.g., 46RE, 47RH).
Import Vehicle Transmission Identification
Honda/Acura: Uses alphanumeric codes like H5DA, SLXA, and B7WA. Identification plates are typically on the transmission case top or side surfaces. Honda often integrates transmission and engine codes, making VIN decoding particularly useful.
Toyota/Lexus: Employs codes like A750E, U660E, and AB60F. Look for stamped numbers on the case or identification plates near the bell housing. Toyota transmissions often include “E” for electronic control or “F” for four-wheel drive variants.
Nissan/Infiniti: Uses codes like RE5R05A, CVT8, and FS5W71C. Identification tags are usually on the case side or top surfaces, with some models using color-coded tags for quick identification.
For detailed specifications and repair procedures for import vehicles, explore our comprehensive Asian brand manual collections including Honda, Toyota, and Nissan documentation.
Advanced Identification Techniques
Electronic Diagnostic Methods
Modern vehicles store transmission information in their electronic control modules. Using an OBD-II scanner, you can access:
- Transmission Control Module (TCM) data: Module part numbers and software versions
- Live transmission data: Gear ratios, shift patterns, and operating parameters
- Stored fault codes: Historical problems that may indicate transmission type
Professional-grade scan tools provide more detailed information than basic code readers. Many auto parts stores offer free diagnostic scans that can reveal transmission-specific information.
For understanding transmission-related diagnostic trouble codes, our DTC Code Diagnostics section provides comprehensive explanations of transmission fault codes and their meanings.
Service History Research
Previous maintenance records often contain transmission information. Check:
- Dealership service records: Often specify exact transmission types and service procedures
- Independent shop records: May include part numbers and fluid specifications
- Previous owner documentation: Maintenance logs and repair receipts
Contact your vehicle’s selling dealer with your VIN—they can often provide complete service history including transmission specifications and any warranty work performed.
Common Identification Challenges and Solutions
Rebuilt or Remanufactured Transmissions
Rebuilt transmissions may retain original case markings while containing updated internal components. Look for:
- Fresh paint or cleaning on the case
- New identification tags or stickers
- Mismatched casting dates and part numbers
- Updated electrical connectors or solenoids
Remanufactured transmissions from reputable suppliers typically include new identification tags with updated part numbers reflecting any improvements or modifications.
Transmission Swaps and Conversions
Modified vehicles present unique identification challenges. Engine/transmission combinations not originally available from the factory require careful inspection:
- Cross-reference engine and transmission compatibility
- Check for custom mounting brackets or modifications
- Look for aftermarket controllers or wiring harnesses
- Identify any adapter plates or custom components
Performance enthusiasts often document modifications, so check online forums specific to your vehicle make and model for common swap configurations.
When to Seek Professional Help
Complex Identification Scenarios
Some situations require professional expertise:
- Heavily modified or custom vehicles
- Rare or exotic transmissions
- Severely damaged identification markings
- European vehicles with complex designation systems
Professional transmission shops have access to specialized databases and identification tools not available to consumers. They can often identify transmissions through internal inspection or specialized testing equipment.
Professional Diagnostic Services
Consider professional identification when:
- DIY methods yield conflicting information
- You’re planning expensive repairs or modifications
- Warranty coverage depends on accurate identification
- Safety-critical systems are involved
Quality transmission specialists typically charge minimal fees for identification services, often applied toward any subsequent work performed.
Using Transmission Information for Maintenance
Fluid Selection and Capacity
Accurate identification ensures proper fluid selection. Key considerations include:
Fluid Type Compatibility:
- Dexron VI vs. Mercon LV specifications
- CVT-specific fluid requirements
- Manual transmission gear oil weights
- Manufacturer-specific formulations
Capacity Requirements:
- Total system capacity (including torque converter)
- Service fill capacity (drain and refill amount)
- Filter change requirements
- Cooler system capacity
Service Intervals:
- Severe service vs. normal driving conditions
- Manufacturer-recommended intervals
- Fluid condition assessment guidelines
For detailed fluid specifications and service procedures, our transmission system guides provide manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules and procedures.
Filter and Parts Compatibility
Transmission identification ensures correct parts ordering:
Internal Filters:
- Spin-on external filters vs. internal screen filters
- Filter kit contents and gasket requirements
- Installation-specific tools and procedures
External Components:
- Solenoid compatibility and programming requirements
- Electrical connector configurations
- Cooler line specifications and routing
Gaskets and Seals:
- Pan gasket materials and configurations
- Pump seal and converter seal specifications
- Internal seal kit compatibility
Troubleshooting Transmission Issues After Identification
Common Problems by Transmission Type
Different transmission families exhibit characteristic failure patterns:
Ford 4R70W Issues:
- Overdrive band failure
- Solenoid body problems
- Forward clutch issues
GM 4L60E Problems:
- 3-4 clutch failure
- Pump rotor wear
- Valve body bore wear
Chrysler 42RLE Concerns:
- Solenoid pack failures
- Overdrive clutch problems
- Valve body issues
Understanding your specific transmission’s common problems helps prioritize maintenance and early problem detection. Our diagnostic troubleshooting guides provide detailed problem-solving procedures for transmission-related issues.
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Monitor these symptoms based on your transmission type:
Automatic Transmission Warnings:
- Delayed engagement when shifting to Drive or Reverse
- Harsh or erratic shifting patterns
- Slipping during acceleration
- Unusual noises during operation
- Fluid leaks or burning odors
Manual Transmission Indicators:
- Difficult shifting or grinding noises
- Clutch slippage or engagement problems
- Gear pop-out under load
- Unusual noises in neutral
CVT-Specific Signs:
- Jerky acceleration or hesitation
- Whining or droning noises
- Sudden loss of acceleration
- Overheating warnings
Resources for Further Information
Manufacturer Resources
Official manufacturer documentation provides the most accurate information:
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Updates and known issues
- Service manuals: Detailed repair procedures and specifications
- Parts catalogs: Correct part numbers and compatibility information
- Training materials: Technical education resources
Many manufacturers provide online access to technical information for registered technicians and some consumer resources.
Online Communities and Forums
Vehicle-specific communities offer real-world experience and identification help:
- Make/model specific forums: Enthusiast communities with deep technical knowledge
- Transmission specialist forums: Professional technician discussions
- DIY repair communities: Hands-on experience sharing
- Social media groups: Quick questions and photo-based identification help
Always verify information from forums with official sources before making repair decisions or parts purchases.
Conclusion
Accurate transmission identification is your foundation for successful maintenance, repair, and modification projects. Whether you use simple VIN decoding, detailed physical inspection, or professional diagnostic services, taking time to properly identify your transmission saves money and prevents costly mistakes.
Start with the easiest methods—VIN decoding and documentation review—before moving to hands-on inspection techniques. When in doubt, professional identification services provide definitive answers and peace of mind for major repair decisions.
Remember that transmission technology continues evolving, with new designs and specifications appearing regularly. Stay informed about your specific transmission type, maintain proper service intervals, and address problems early to maximize transmission life and performance.
Ready to access detailed repair information for your transmission? Explore our comprehensive manual collections for manufacturer-specific service procedures, troubleshooting guides, and technical specifications. From basic maintenance to complete overhauls, having the right information ensures successful repairs and reliable operation.
Disclaimer: This information is provided for reference purposes only. Always consult manufacturer specifications and qualified professionals for critical repair decisions. Implement procedures at your own risk and responsibility, prioritizing safety throughout all maintenance and repair activities.
