When your vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) kicks in during an emergency stop, a complex hydraulic valve assembly is working behind the scenes to prevent wheel lockup and maintain steering control. The ABS valve assembly, also known as the hydraulic control unit (HCU), is one of the most critical safety components in modern vehicles. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, ABS systems reduce fatal crash risk by up to 6% and serious injury crashes by 5%, making the proper function of every ABS component essential for road safety.
The ABS valve assembly controls brake pressure to individual wheels with split-second precision, preventing dangerous skids and maintaining vehicle stability. However, when this sophisticated component begins to fail, drivers may experience symptoms ranging from dashboard warning lights to complete brake system compromise. Understanding how to identify, diagnose, and address ABS valve assembly problems can mean the difference between a safe stop and a dangerous situation.
This comprehensive guide provides both DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians with the technical knowledge needed to understand ABS valve assembly operation, recognize failure symptoms, and make informed decisions about repair versus replacement. We’ll cover everything from basic system operation to advanced diagnostic procedures, always prioritizing safety and proper professional consultation when dealing with critical brake system components.
Important Safety Disclaimer: The ABS valve assembly is a critical safety component. While this article provides educational information about ABS valve assembly diagnosis and maintenance, any work involving brake system components should be performed by qualified professionals. Improper brake system service can result in complete brake failure, serious injury, or death. Always consult professional technicians for brake system repairs and follow all safety protocols.
Understanding the ABS Valve Assembly: How Your Braking Safety System Works
The Anti-Lock Braking System Explained
The anti-lock braking system represents one of the most significant advances in automotive safety technology. Developed to prevent wheel lockup during hard braking, ABS allows drivers to maintain steering control while bringing their vehicle to the shortest possible stop. The system monitors wheel speed continuously and modulates brake pressure when it detects impending wheel lock conditions.
Modern ABS systems are legally required on all passenger vehicles manufactured after September 1, 2000, in the United States, and similar regulations exist in Canada and Australia. The technology has evolved significantly since its introduction, with today’s systems integrating with electronic stability control (ESC) and traction control systems to provide comprehensive vehicle stability management.
The ABS valve assembly serves as the central hydraulic control point for the entire anti-lock braking system. When the ABS control module detects wheel lockup conditions through wheel speed sensor data, it commands the valve assembly to modulate brake pressure to the affected wheels. This process occurs up to 15 times per second, creating the characteristic pulsing sensation drivers feel in the brake pedal during ABS operation.
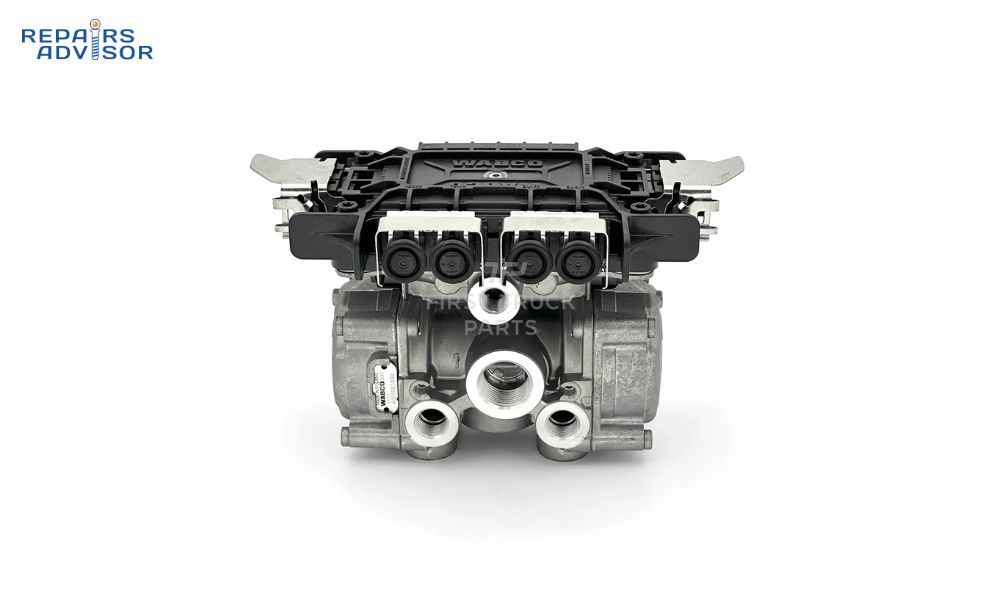
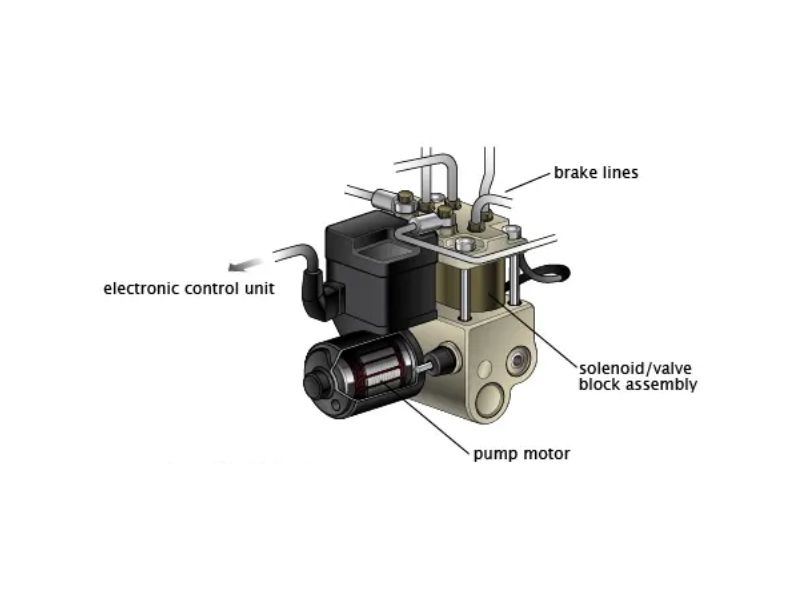
Inside the ABS Valve Assembly: Critical Components Breakdown
The ABS valve assembly is a sophisticated hydraulic and electronic component housing multiple critical subsystems. Understanding these components helps in diagnosing problems and appreciating the complexity of modern brake systems.
Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) forms the main body of the ABS valve assembly. This precision-machined aluminum or steel housing contains multiple hydraulic passages, valve seats, and mounting points for electronic components. The HCU must withstand brake system pressures up to 2,000 PSI while maintaining precise pressure control across multiple brake circuits.
Solenoid Valves within the assembly control brake fluid flow to individual wheels or brake circuits. Most systems use two solenoid valves per controlled wheel: an inlet valve that controls fluid flow from the master cylinder to the brake caliper, and an outlet valve that releases pressure from the caliper back to a low-pressure accumulator. These electromagnetic valves operate under direct control from the ABS control module.
Accumulator serves as a temporary brake fluid reservoir during ABS operation. When the outlet solenoids release pressure from brake calipers, this fluid must be stored temporarily before being returned to the master cylinder. The accumulator also helps smooth pressure pulses and provides consistent system operation.
Pump Motor generates hydraulic pressure to return brake fluid from the accumulator back to the master cylinder or brake circuits. This high-speed electric motor drives a hydraulic pump that can generate pressures exceeding master cylinder output when necessary. The pump motor is one of the most commonly replaced ABS valve assembly components due to its high-stress operating environment.
Pressure Sensors monitor hydraulic pressure at various points within the system. These sensors provide feedback to the ABS control module, allowing precise pressure control and system monitoring. Pressure sensor failure can cause erratic ABS operation or complete system shutdown.
Electronic Control Module Integration connects the valve assembly to the vehicle’s ABS control computer. Multiple electrical connections carry solenoid control signals, sensor data, and diagnostic communication. The wiring harness and connectors are critical points that can fail due to corrosion, vibration, or environmental exposure.
How ABS Valve Assembly Controls Brake Pressure
During normal braking operation, the ABS valve assembly remains passive. Brake fluid flows directly from the master cylinder through the inlet solenoids (which remain open) to the brake calipers. The outlet solenoids remain closed, maintaining full brake pressure as applied by the driver. The pump motor remains off, and the system operates like a conventional brake system.
When wheel speed sensors detect impending lockup, the ABS control module commands the valve assembly into action. The process occurs in three distinct phases: pressure hold, pressure decrease, and pressure increase. During pressure hold, the inlet solenoid closes while the outlet solenoid remains closed, maintaining current brake pressure. For pressure decrease, the outlet solenoid opens while the inlet remains closed, releasing brake fluid from the caliper to the accumulator. Finally, during pressure increase, the inlet solenoid opens while the outlet closes, and the pump motor may activate to restore or increase brake pressure.
This cycle repeats rapidly, creating the characteristic ABS pedal pulsation. The system can modulate pressure independently on each controlled wheel, allowing optimal braking force while maintaining vehicle control. Modern systems can complete this cycle up to 15 times per second, providing extremely precise brake pressure control.
Communication with wheel speed sensors is critical for proper ABS valve assembly operation. The control module compares wheel speeds continuously, detecting when one wheel begins to decelerate faster than others, indicating impending lockup. The valve assembly responds within milliseconds to prevent wheel lock while maintaining maximum braking effectiveness.
Fail-safe mechanisms protect against complete brake system failure if the ABS valve assembly malfunctions. Most systems default to conventional braking operation if ABS components fail, ensuring basic brake function remains available. However, this backup operation may not provide optimal stopping performance and typically activates dashboard warning lights to alert the driver.
Signs Your ABS Valve Assembly Is Failing: Critical Warning Indicators
Immediate Warning Signs of ABS Valve Assembly Problems
ABS Warning Light Activation represents the most obvious indicator of ABS valve assembly problems. The amber ABS warning light on your dashboard illuminates when the system detects faults within the anti-lock braking system. However, the warning light alone doesn’t specify whether the problem lies with the valve assembly, sensors, or control module. Consistent ABS light activation requires professional diagnosis to determine the root cause.
Some vehicles display additional warning patterns that can indicate valve assembly-specific problems. Intermittent ABS light activation during startup may indicate pump motor problems within the valve assembly. Lights that activate only during braking or ABS operation often point to solenoid valve or pressure sensor issues. Modern vehicles may also display traction control or stability control warning lights when ABS valve assembly problems affect these integrated systems.
Brake Pedal Behavior Changes often accompany ABS valve assembly failure. A spongy or soft brake pedal may indicate internal leakage within the valve assembly, allowing brake fluid to bypass normal hydraulic circuits. Conversely, an unusually hard brake pedal might suggest pump motor failure or accumulator problems preventing proper pressure modulation.
Abnormal brake pedal pulsation outside of ABS activation can indicate stuck or malfunctioning solenoid valves. This pulsation differs from normal ABS operation, occurring during gentle braking when ABS shouldn’t activate. The pulsation may be more pronounced or irregular compared to proper ABS function.
Unusual Braking Sounds frequently accompany ABS valve assembly problems. A continuous whining or buzzing noise from the ABS valve assembly area may indicate pump motor problems. The pump motor should operate only briefly during startup self-tests or ABS activation. Continuous operation suggests internal leakage requiring constant pressure maintenance.
Clicking or ticking sounds during braking may indicate solenoid valve problems. These electromagnetic valves produce subtle clicking sounds during normal ABS operation, but abnormal clicking during regular braking suggests valve malfunction. Grinding or squealing sounds typically indicate mechanical problems within the valve assembly housing.
Inconsistent Brake Response manifests as unpredictable brake pedal feel or stopping performance. The brake pedal may sink gradually during sustained braking, indicating internal valve assembly leakage. Alternatively, brake response may vary between applications, sometimes feeling normal and other times requiring excessive pedal pressure.
Uneven braking between wheels can result from individual solenoid valve failures within the ABS valve assembly. One wheel may receive inadequate brake pressure while others operate normally, causing the vehicle to pull during braking. This condition is particularly dangerous and requires immediate professional attention.
Brake Fluid Issues often accompany ABS valve assembly problems. Brake fluid leakage around the valve assembly mounting area indicates seal failure or housing damage. The complex internal passages and high operating pressures make the valve assembly prone to internal leakage that may not be immediately visible.
Rapid brake fluid consumption without visible external leaks may suggest internal valve assembly problems. Brake fluid bypassing normal circuits within the valve assembly can cause fluid level drops and require frequent refilling. Contaminated brake fluid with metal particles or unusual color changes can indicate internal valve assembly wear.
Secondary Indicators and System-Wide Effects
Traction Control Malfunction frequently accompanies ABS valve assembly problems because most modern systems share components between ABS and traction control functions. Traction control systems use the same wheel speed sensors and often utilize ABS valve assembly components to control wheel spin. When the valve assembly fails, both systems may become inoperative.
Dashboard warning lights for traction control, stability control, or electronic stability programs (ESP) may illuminate alongside ABS warnings. These systems depend on the ABS valve assembly’s ability to modulate brake pressure independently at each wheel. Valve assembly failure compromises these advanced safety systems, leaving drivers with basic brake function only.
Electronic Stability Control Issues represent serious safety concerns when related to ABS valve assembly failure. ESC systems prevent vehicle rollover and loss of control by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. Without proper ABS valve assembly function, ESC cannot provide this critical safety intervention. Drivers may notice reduced vehicle stability during emergency maneuvers or adverse weather conditions.
The integration between ABS, traction control, and stability systems means that valve assembly problems can disable multiple safety systems simultaneously. This system-wide failure significantly increases accident risk and requires immediate professional attention.
Brake Performance Degradation may occur gradually as ABS valve assembly components wear. Drivers might notice increased stopping distances, particularly on wet or slippery surfaces where ABS provides the greatest benefit. Without proper ABS function, wheels may lock during hard braking, causing loss of steering control and longer stopping distances.
Emergency braking performance suffers most dramatically when ABS valve assembly problems prevent proper pressure modulation. The characteristic pulse sensation of ABS operation may be absent, replaced by wheel lockup and potential loss of vehicle control.
Intermittent System Function creates particularly dangerous conditions because drivers cannot predict when ABS will be available. The valve assembly may function normally during light braking but fail under heavy braking conditions when ABS is most needed. This intermittent operation often results from marginal component failure that worsens under high-stress conditions.
Temperature-related intermittent problems are common with ABS valve assemblies. Cold weather may cause seals to contract, creating temporary leakage, while hot weather can cause electronic components to malfunction. These temperature-sensitive failures often worsen over time until complete system failure occurs.
Pressure Loss Symptoms indicate serious ABS valve assembly internal leakage. The brake pedal may gradually sink to the floor during sustained braking as brake fluid bypasses normal circuits within the valve assembly. This condition represents a serious safety hazard requiring immediate professional attention.
Complete brake system failure, while rare, can result from catastrophic ABS valve assembly failure. Internal valve assembly damage can block brake fluid flow or cause massive fluid loss, compromising basic brake function. This condition requires immediate vehicle shutdown and professional service.
Environmental and Usage Factors That Accelerate ABS Valve Assembly Wear
Climate Impacts significantly affect ABS valve assembly longevity. Extreme temperature variations cause expansion and contraction of metal components and seals, leading to internal leakage over time. Cold climates are particularly harsh on ABS valve assemblies due to brake fluid viscosity changes and ice formation that can damage external components.
Moisture infiltration represents a major threat to ABS valve assembly electronics and hydraulic components. High humidity environments can cause corrosion of electrical connections and contamination of brake fluid. Salt air in coastal regions accelerates corrosion of valve assembly housings and mounting hardware.
Road salt used for winter driving creates highly corrosive conditions for ABS valve assemblies. Salt spray can penetrate electrical connections and cause accelerated wear of external components. Regular undercarriage washing is essential in salt-exposed regions to prevent premature valve assembly failure.
Driving Conditions play a crucial role in ABS valve assembly wear patterns. Stop-and-go traffic generates frequent brake system thermal cycling that stresses valve assembly seals and electronic components. Mountain driving with frequent ABS activation accelerates solenoid valve and pump motor wear due to increased operating cycles.
Commercial vehicle operation or frequent heavy loading increases brake system pressures and operating temperatures, accelerating ABS valve assembly wear. Fleet vehicles and delivery trucks often experience premature valve assembly failure due to severe duty cycles and high annual mileage.
Aggressive driving habits that frequently trigger ABS operation cause premature component wear within the valve assembly. Racing, emergency braking practice, or intentional ABS activation significantly reduces valve assembly service life.
Maintenance Neglect represents the most preventable cause of premature ABS valve assembly failure. Contaminated brake fluid damages internal valve components and seals, leading to leakage and malfunction. Brake fluid should be replaced according to manufacturer intervals, typically every 2-3 years or 30,000-50,000 miles.
Ignoring ABS system warning lights allows minor problems to develop into major valve assembly failures. Early intervention can often prevent complete valve assembly replacement, saving significant repair costs and maintaining vehicle safety.
Postponing brake system maintenance, such as brake pad replacement, can lead to excessive heat generation that damages ABS valve assembly components. Overheated brake systems stress all components, including the sophisticated ABS valve assembly.
Age-Related Deterioration affects all ABS valve assemblies regardless of usage patterns. Rubber seals and O-rings within the valve assembly deteriorate over time, causing internal leakage and pressure loss. Most ABS valve assemblies require service or replacement between 100,000-150,000 miles, depending on operating conditions.
Electronic component aging affects solenoid valves and pressure sensors within the valve assembly. Temperature cycling and electrical stress cause gradual degradation of electronic components, leading to erratic operation and eventual failure.
Corrosion of internal passages can occur even with proper brake fluid maintenance due to microscopic water absorption over time. This internal corrosion can block passages or damage precision-machined surfaces within the valve assembly.
For comprehensive brake system resources and related diagnostic information, explore our Vehicle Systems & Parts Explained section for additional technical guidance.
Professional ABS Valve Assembly Diagnosis: Step-by-Step Testing Procedures
Essential Diagnostic Equipment for ABS Valve Testing
OBD-II Scanner Requirements for ABS valve assembly diagnosis extend beyond basic code readers. Professional ABS diagnosis requires scan tools capable of accessing ABS control modules, reading live data streams, and performing actuator tests. Generic OBD-II scanners often cannot communicate with ABS systems, making manufacturer-specific or professional-grade diagnostic equipment essential.
Advanced scan tools should provide bi-directional control capabilities, allowing technicians to command individual solenoid valves and pump motors within the ABS valve assembly. This actuator testing capability helps isolate specific component failures within the valve assembly. Live data monitoring during test drives reveals intermittent problems that static testing might miss.
ABS-capable scan tools must display wheel speed sensor data, brake pressure readings, and solenoid valve command status. This information helps technicians understand whether problems lie within the valve assembly itself or in related sensors and wiring. Professional diagnostic equipment also provides component specifications and testing procedures specific to each vehicle application.
Pressure Testing Equipment enables direct measurement of hydraulic pressures within the ABS valve assembly. Professional brake system pressure gauges with appropriate fittings allow technicians to measure accumulator pressure, pump output pressure, and individual circuit pressures. These measurements help identify internal leakage, pump motor problems, and pressure sensor failures.
Pressure testing requires specialized adapters and fittings compatible with specific ABS valve assembly designs. Each manufacturer uses different connection types and pressure port locations, necessitating comprehensive adapter sets. Pressure testing equipment must handle brake system pressures up to 3,000 PSI safely and accurately.
Digital pressure gauges with data logging capabilities help identify intermittent pressure problems during extended testing. The ability to record pressure variations over time reveals problems that might not be apparent during brief static tests.
Electrical Testing Tools for ABS valve assembly diagnosis include digital multimeters, oscilloscopes, and specialized wiring diagram access. Solenoid valve resistance testing requires precise ohm measurements to identify open circuits, short circuits, or abnormal resistance values. Most ABS solenoid valves operate within specific resistance ranges that vary by manufacturer and design.
Oscilloscopes help analyze solenoid valve operation by displaying command signals and valve response patterns. This advanced testing reveals timing problems, voltage irregularities, and electromagnetic interference that can affect valve assembly operation. Pressure waveform analysis using pressure transducers and oscilloscopes provides detailed insight into valve assembly hydraulic performance.
Wiring diagram access through manufacturer service information or professional databases is essential for proper electrical diagnosis. ABS valve assembly wiring harnesses contain multiple circuits with complex interconnections that require accurate documentation for effective troubleshooting.
Safety Equipment for ABS valve assembly testing includes proper eye protection, hydraulic-resistant gloves, and appropriate clothing. Brake fluid under high pressure can cause serious injury if proper safety precautions are not followed. Work areas must be well-ventilated and equipped with appropriate brake fluid spill containment materials.
Professional brake bleeding equipment helps maintain system pressure during testing and prevents air introduction during diagnostic procedures. Pressure bleeding systems are particularly important when testing ABS valve assemblies because air contamination can mask hydraulic problems and affect test results.
Vehicle lifting equipment must be adequate for safe undercar access to ABS valve assemblies. Most valve assemblies are mounted in protected locations requiring vehicle lifting for proper access. Jack stands or professional lifts must be properly positioned to ensure technician safety during extended diagnostic procedures.
Vehicle Service Information provides essential technical data for proper ABS valve assembly diagnosis. Manufacturer service manuals contain component specifications, wiring diagrams, diagnostic procedures, and troubleshooting charts specific to each vehicle application. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and proper repair procedures.
Technical service bulletins (TSBs) document known problems and updated diagnostic procedures for specific ABS valve assembly applications. These bulletins often contain valuable diagnostic shortcuts and repair procedures not found in standard service manuals. Professional technicians regularly check for updated TSBs related to ABS valve assembly problems.
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) definitions and diagnostic procedures vary significantly between manufacturers and model years. Professional diagnostic databases provide current, accurate information essential for effective ABS valve assembly troubleshooting.
Comprehensive ABS Valve Assembly Testing Sequence
Step 1: Visual Inspection
External valve assembly examination begins with a thorough inspection of the valve assembly housing, mounting brackets, and surrounding components. Look for obvious signs of brake fluid leakage, corrosion, physical damage, or contamination. ABS valve assemblies are typically mounted in protected locations, but road debris, collision damage, or corrosion can affect external components.
Pay particular attention to electrical connections and wiring harnesses. Corrosion, moisture intrusion, or physical damage to electrical connections can cause intermittent or complete ABS valve assembly failure. Connector pins should be clean, properly seated, and free from corrosion or damage.
Brake fluid level and condition assessment provides important clues about ABS valve assembly health. Low brake fluid levels may indicate internal valve assembly leakage, while contaminated or discolored brake fluid suggests system maintenance neglect that can damage valve assembly components.
Mounting bracket and hardware condition affects valve assembly operation and longevity. Loose mounting bolts can cause vibration damage to internal components, while corroded brackets may allow excessive movement during ABS operation. All mounting hardware should be properly torqued and in good condition.
Step 2: Electronic Diagnosis
OBD-II error code retrieval provides the starting point for electronic diagnosis of ABS valve assembly problems. Most ABS valve assembly failures generate specific diagnostic trouble codes that help focus diagnostic efforts. However, multiple codes may be present, requiring systematic analysis to identify root causes versus symptom codes.
Common ABS valve assembly related codes include pump motor circuit faults, solenoid valve circuit problems, and pressure sensor malfunctions. Each code requires specific diagnostic procedures outlined in manufacturer service information. Code interpretation should consider the relationship between multiple codes and system operation.
Live data monitoring during test drives reveals dynamic problems that static testing cannot detect. Monitor wheel speed sensor inputs, brake pressure readings, solenoid valve commands, and pump motor operation during various driving conditions. Pay particular attention to data during ABS activation and system startup procedures.
Actuator testing using diagnostic equipment allows individual testing of solenoid valves and pump motors within the ABS valve assembly. This testing helps isolate specific component failures and verify proper valve assembly operation. Each solenoid valve should operate smoothly with proper current draw and response time.
Electrical circuit continuity and resistance testing verifies proper wiring harness condition and component electrical integrity. Solenoid valve resistance should match manufacturer specifications, typically ranging from 2-6 ohms depending on design. Pressure sensor circuits should provide proper voltage references and signal ranges.
Step 3: Hydraulic Testing
System pressure testing at idle and under load reveals hydraulic problems within the ABS valve assembly. Accumulator pressure should build to specification during startup and maintain pressure during system operation. Low accumulator pressure may indicate pump motor problems or internal leakage.
Individual circuit pressure testing helps identify specific valve assembly problems affecting certain wheels or brake circuits. Each brake circuit should maintain proper pressure relationships and respond correctly to ABS commands. Pressure variations between circuits may indicate internal valve assembly problems.
Pressure accumulation and release cycle testing evaluates pump motor performance and accumulator function. The pump motor should cycle on and off to maintain proper accumulator pressure without excessive run time. Continuous pump operation indicates internal leakage requiring valve assembly service or replacement.
Brake fluid flow and restriction analysis helps identify internal blockages or restrictions within the valve assembly. Flow testing requires specialized equipment but can reveal problems not apparent through pressure testing alone. Internal restrictions can cause delayed ABS response or incomplete pressure relief.
Step 4: Functional Testing
Controlled ABS activation testing in a safe environment verifies overall system operation and valve assembly response. This testing should be performed in a controlled area with proper safety precautions and may require special procedures outlined in manufacturer service information.
Brake pedal feel and response evaluation during ABS testing provides important diagnostic information. The brake pedal should pulse normally during ABS activation and return to normal feel when ABS deactivates. Abnormal pedal behavior may indicate valve assembly internal problems.
System response time measurement helps identify sluggish valve assembly operation that may not be apparent during normal operation. ABS systems should activate within milliseconds of detecting wheel lockup conditions. Delayed response may indicate component wear or hydraulic problems within the valve assembly.
Integration testing with related safety systems verifies proper communication between ABS valve assembly and traction control or stability control systems. These integrated systems share components and communication networks, making comprehensive testing essential for proper diagnosis.
To learn more about related brake system components and their diagnostic procedures, visit our comprehensive guide on Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Why It Is Important and How It Works.
Common Diagnostic Pitfalls: Avoiding ABS Valve Assembly Testing Errors
Mistaking Symptoms for Other Brake System Components represents one of the most common diagnostic errors. ABS valve assembly problems can mimic master cylinder, brake booster, or even brake pad problems. Proper systematic diagnosis prevents unnecessary component replacement and ensures accurate problem identification.
Brake pedal symptoms, in particular, can be misleading because multiple brake system components affect pedal feel and response. A thorough understanding of brake system operation and proper diagnostic procedures prevents misdiagnosis and unnecessary expense.
Insufficient Diagnostic Equipment leading to incomplete testing often results in incorrect diagnosis or missed problems. Basic code readers cannot access ABS systems, while inadequate pressure testing equipment may not reveal internal valve assembly problems. Professional diagnosis requires appropriate equipment and technical expertise.
Generic scan tools may not provide sufficient data depth for complex ABS valve assembly diagnosis. Manufacturer-specific diagnostic equipment often reveals problems that generic tools cannot detect. Investment in proper diagnostic equipment is essential for accurate ABS valve assembly service.
Environmental Factors Affecting Test Results can lead to incorrect diagnosis if not properly considered. Temperature, humidity, and road conditions all affect ABS system operation and diagnostic test results. Testing should be performed under various conditions when intermittent problems are suspected.
Intermittent problems are particularly challenging because they may not be present during diagnostic testing. Extended testing periods and data logging may be necessary to capture intermittent ABS valve assembly problems. Customer interview information about when problems occur is crucial for effective diagnosis.
Intermittent Fault Challenges and Documentation Requirements necessitate careful documentation of symptoms, test results, and repair procedures. Intermittent ABS valve assembly problems may require multiple diagnostic sessions and customer follow-up to verify complete repair.
Professional diagnostic documentation should include all test results, component specifications, and repair procedures performed. This documentation helps track problem patterns and provides valuable information for warranty claims or future service needs.
ABS Valve Assembly Repair Options: When to Repair vs. Replace
Determining If ABS Valve Assembly Repair Is Possible
Repairable Conditions for ABS valve assemblies are limited due to the complex internal construction and precision requirements of these components. Minor external seal leaks may be repairable with appropriate seal kits if the valve assembly housing is undamaged. Some manufacturers provide seal kits for specific valve assembly applications, though availability varies significantly.
Solenoid valve cleaning may resolve certain types of contamination-related problems within the valve assembly. Brake fluid contamination can cause solenoid valve sticking or erratic operation that cleaning procedures might correct. However, solenoid valve cleaning requires complete valve assembly disassembly and should only be attempted by experienced technicians.
Electrical connection issues, including corroded terminals or damaged wiring harnesses, are typically repairable without valve assembly replacement. These repairs require proper electrical repair procedures and materials to ensure long-term reliability. Connection repairs must meet manufacturer specifications for current capacity and environmental protection.
Non-Repairable Conditions include most internal component failures within the ABS valve assembly. Internal valve damage, such as scored valve seats or damaged solenoid valve components, typically requires complete valve assembly replacement. The precision manufacturing tolerances required for proper ABS operation make internal component repair impractical in most cases.
Pump motor failure within the ABS valve assembly almost always requires complete unit replacement. The pump motor is typically not available as a separate component, and the labor required for replacement often exceeds the cost of a complete valve assembly. Pump motor problems usually indicate other internal problems requiring comprehensive service.
Housing cracks or casting porosity in the valve assembly body cannot be effectively repaired due to the high operating pressures and precision passages involved. Any compromise in housing integrity requires complete valve assembly replacement to ensure reliable operation and safety.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for ABS valve assembly repair versus replacement must consider several factors beyond initial component cost. Labor time for repair attempts may exceed replacement time, particularly if repair attempts are unsuccessful. The risk of repeat failures with repaired components may justify replacement despite higher initial cost.
Warranty considerations favor replacement over repair in most cases. New or remanufactured valve assemblies typically include comprehensive warranties, while repairs may have limited warranty coverage. The liability implications of brake system repairs also favor replacement when internal component integrity is questionable.
Reliability Considerations after repair must account for the critical safety role of ABS valve assemblies. Even successful repairs may not provide the long-term reliability expected from safety-critical brake system components. The potential consequences of ABS failure during emergency braking situations often justify replacement over repair attempts.
Component availability for repair parts varies significantly between manufacturers and valve assembly designs. Some valve assemblies have no available repair parts, making replacement the only viable option. Others may have limited seal kit availability but no internal component replacement options.
Professional ABS Valve Assembly Replacement Process
Pre-Replacement Preparation for ABS valve assembly replacement requires careful system depressurization and safety procedures. ABS systems operate under high pressure, and proper depressurization prevents injury and brake fluid contamination during service. Most systems require specific depressurization procedures outlined in manufacturer service information.
Battery disconnection is typically required before ABS valve assembly replacement to prevent accidental system activation during service. Some systems require specific shutdown procedures to prevent control module damage or system calibration loss. Follow manufacturer procedures exactly to prevent expensive collateral damage.
Brake fluid drainage and contamination prevention procedures help ensure clean installation and prevent system contamination. New brake fluid should be available for system refilling, and proper fluid disposal procedures must be followed. Contaminated brake fluid can damage the new valve assembly and cause premature failure.
Component Removal procedures for ABS valve assemblies vary significantly between vehicle applications. Brake line disconnection requires proper line wrenches and careful technique to prevent fitting damage. Brake lines are typically made from steel tubing with specific torque requirements and may require special tools for removal and installation.
Electrical harness removal requires careful connector handling to prevent pin damage or seal displacement. Some connectors have locking mechanisms or secondary locks that must be properly released before disconnection. Document connector positions and routing before removal to ensure proper reassembly.
Access to ABS valve assemblies often requires removal of other components, such as air cleaner assemblies, battery trays, or body panels. Some installations require significant disassembly for valve assembly access, making labor time a significant cost factor in replacement procedures.
Installation Requirements include proper torque specifications for mounting bolts and brake line fittings. ABS valve assemblies are typically mounted with specific torque requirements to prevent stress concentration or vibration problems. Improper mounting can cause premature failure or noise problems.
Brake line connection torque specifications are critical for preventing leaks and ensuring proper system operation. Over-tightening can damage fittings or brake lines, while under-tightening can cause dangerous leaks. Use proper torque wrenches and follow manufacturer specifications exactly.
Electrical connection procedures require proper connector seating and locking mechanism engagement. Improperly connected electrical harnesses can cause intermittent operation or complete system failure. Verify proper connection by checking for secure engagement and proper connector alignment.
System Bleeding after ABS valve assembly replacement requires specific procedures that differ from conventional brake bleeding. ABS systems contain internal passages and chambers that require special bleeding procedures to remove all air from the system. Conventional bleeding procedures may not remove all air from ABS valve assemblies.
Many ABS systems require pressure bleeding or scan tool-activated bleeding procedures to ensure complete air removal. These procedures may require specific equipment and technical knowledge beyond basic brake service capabilities. Improper bleeding can cause spongy brake pedal feel or reduced braking effectiveness.
Some systems require specific bleeding sequences that start with the ABS valve assembly and proceed to individual wheels in a prescribed order. Other systems may require multiple bleeding cycles or specific scan tool activation procedures during bleeding. Always follow manufacturer bleeding procedures exactly.
Post-Installation Testing must verify proper ABS valve assembly operation and integration with related systems. This testing should include scan tool verification of proper system communication, pressure testing to verify proper hydraulic operation, and road testing to confirm proper ABS activation and pedal feel.
Functional testing should include controlled ABS activation in a safe environment to verify proper system operation. The brake pedal should exhibit normal ABS pulsation, and the system should deactivate properly when wheel lockup conditions end. Any abnormal operation requires further diagnosis and correction.
System calibration procedures may be required after ABS valve assembly replacement. Some systems require scan tool procedures to initialize the new valve assembly or clear adaptation values stored in the control module. These procedures are essential for proper system operation and must be performed according to manufacturer instructions.
DIY vs. Professional Service Decision Matrix
DIY Suitable Tasks
Basic Visual Inspection and Cleaning of ABS valve assembly external components represents appropriate DIY maintenance for mechanically inclined individuals. External cleaning can help identify leaks, corrosion, or damage that might indicate internal problems. This inspection should focus on obvious external problems without disassembling system components.
Cleaning electrical connections and applying appropriate dielectric grease can help prevent corrosion-related problems. However, electrical connection service should be limited to external cleaning and corrosion prevention without disassembling connectors or modifying wiring.
Electrical Connector Maintenance includes visual inspection for corrosion, damage, or improper seating. Basic multimeter testing of connector continuity may be appropriate for experienced DIY enthusiasts with proper equipment and technical knowledge. However, this testing should be limited to basic continuity checks without attempting to measure component specifications.
Brake Fluid Level Monitoring and condition assessment provides early warning of potential ABS valve assembly problems. Regular brake fluid level checks can identify gradual fluid loss that might indicate internal valve assembly leakage. Brake fluid condition assessment can reveal contamination that threatens valve assembly components.
Error Code Reading and Documentation using basic OBD-II scanners can provide valuable diagnostic information for professional technicians. However, ABS-specific codes may not be accessible with basic scanners, and code interpretation requires technical knowledge beyond typical DIY capabilities.
Professional Required Tasks
Complete Valve Assembly Replacement requires specialized tools, technical knowledge, and safety procedures beyond typical DIY capabilities. The hydraulic complexity and safety-critical nature of ABS valve assemblies make professional replacement essential for proper installation and system safety.
Brake system bleeding procedures for ABS systems require specific equipment and procedures that differ significantly from conventional brake bleeding. Improper bleeding can result in brake system failure or reduced effectiveness, making professional service essential for safety.
Hydraulic System Pressure Testing requires specialized equipment and technical knowledge to perform safely and accurately. High-pressure hydraulic testing poses injury risks and requires professional-grade equipment for accurate diagnosis.
Advanced Electrical Diagnostics including solenoid valve testing, pressure sensor verification, and wiring harness diagnosis require professional diagnostic equipment and technical expertise. Misdiagnosis can result in unnecessary component replacement and continued safety system problems.
Warranty and Liability Considerations make professional service advisable for critical safety systems like ABS valve assemblies. Professional technicians carry liability insurance and provide warranty coverage for safety-critical brake system repairs. DIY brake system work may void vehicle warranties and create liability concerns in case of accidents.
For vehicle-specific ABS valve assembly service procedures and technical specifications, consult our comprehensive Service Manuals collection for detailed professional repair information.
Preventing ABS Valve Assembly Failure: Maintenance Best Practices
Essential ABS System Maintenance for Valve Assembly Longevity
Brake Fluid Service Intervals represent the most critical maintenance factor for ABS valve assembly longevity. Manufacturer recommendations typically specify brake fluid replacement every 2-3 years or 30,000-50,000 miles, whichever comes first. However, severe operating conditions may require more frequent service intervals to prevent valve assembly damage from contaminated brake fluid.
Real-world brake fluid service intervals should consider environmental factors and driving conditions that accelerate fluid degradation. Vehicles operated in high-humidity environments, extreme temperatures, or dusty conditions may require annual brake fluid service to prevent ABS valve assembly contamination. Commercial vehicles and high-mileage applications typically benefit from shortened service intervals.
Brake fluid absorbs moisture from the atmosphere over time, reducing its boiling point and creating corrosive conditions within the ABS valve assembly. Moisture-contaminated brake fluid can cause internal corrosion, seal deterioration, and electronic component damage within the valve assembly. Regular fluid replacement prevents these problems and maintains optimal system performance.
System Inspection Schedule should include regular visual inspection of ABS valve assembly external components, electrical connections, and mounting hardware. Monthly visual inspections can identify developing problems before they cause complete system failure. Professional inspection during routine maintenance intervals provides more comprehensive system evaluation.
Annual professional inspection should include scan tool diagnostic testing, brake fluid condition assessment, and functional testing of ABS operation. This comprehensive inspection can identify marginal components before they fail completely, allowing planned replacement rather than emergency repairs.
Seasonal inspection schedules work well for vehicles exposed to harsh winter conditions. Pre-winter inspection ensures system readiness for challenging driving conditions, while post-winter inspection identifies salt corrosion or other environmental damage requiring attention.
Environmental Protection measures help extend ABS valve assembly service life in harsh operating conditions. Regular undercarriage washing removes salt, chemicals, and debris that can accelerate valve assembly deterioration. This protection is particularly important for vehicles operated in coastal areas or regions with winter road salt application.
Corrosion prevention treatments applied to ABS valve assembly mounting areas and electrical connections can significantly extend component life. Professional undercoating or corrosion inhibitor application provides long-term protection against environmental damage.
Performance Monitoring involves recognizing early warning signs of valve assembly problems before complete failure occurs. Dashboard warning light activation, changes in brake pedal feel, or unusual sounds during braking require immediate professional evaluation. Early intervention often prevents complete valve assembly failure and reduces repair costs.
Driver education about normal ABS operation helps identify abnormal system behavior that might indicate developing problems. Understanding normal ABS pedal pulsation, activation frequency, and system sounds helps drivers recognize when professional evaluation is needed.
Critical Brake Fluid Management for ABS Valve Assembly Health
Fluid Type Specifications for ABS systems require strict adherence to manufacturer recommendations. DOT 3, DOT 4, and DOT 5.1 brake fluids have different chemical compositions and performance characteristics that affect ABS valve assembly compatibility. Using incorrect brake fluid types can damage seals, corrode internal components, or cause system malfunction.
DOT 5 silicone-based brake fluid is incompatible with most ABS systems and should never be used unless specifically recommended by the manufacturer. Mixing different brake fluid types can cause chemical reactions that damage ABS valve assembly components and compromise system safety.
Manufacturer-specific brake fluid requirements may exceed standard DOT specifications for certain high-performance or heavy-duty applications. Always use brake fluid meeting or exceeding manufacturer specifications to ensure proper ABS valve assembly operation and warranty compliance.
Contamination Prevention requires careful handling procedures during brake fluid service and system maintenance. Brake fluid containers should be kept sealed and protected from moisture contamination. Open containers absorb moisture rapidly, reducing fluid quality and potentially damaging ABS valve assembly components.
System contamination during service can introduce particles, water, or incompatible fluids that damage precision ABS valve assembly components. Use only clean funnels, containers, and tools when servicing brake systems. Any contamination can cause expensive valve assembly damage and system failure.
Air contamination during brake fluid service can cause spongy brake pedal feel and reduced ABS effectiveness. Proper bleeding procedures and contamination prevention during service maintain system integrity and prevent premature valve assembly problems.
Replacement Timing should prioritize condition-based service over strict mileage intervals when possible. Brake fluid test strips or electronic testers can assess fluid condition and water content, indicating when replacement is necessary regardless of mileage or time intervals.
Age-based replacement intervals remain important even for low-mileage vehicles because brake fluid deteriorates over time regardless of usage. Vehicles driven infrequently may require brake fluid replacement based on time intervals rather than mileage to prevent ABS valve assembly damage from aged fluid.
Emergency replacement may be necessary if brake fluid becomes contaminated with water, petroleum products, or other incompatible materials. Contaminated brake fluid can cause immediate damage to ABS valve assembly components and requires immediate system flushing and fluid replacement.
Quality Testing helps determine optimal brake fluid replacement intervals and verify proper fluid condition after service. Professional brake fluid testing equipment can measure water content, boiling point, and chemical condition to assess replacement needs accurately.
Copper content testing indicates brake fluid degradation and internal system corrosion that can damage ABS valve assembly components. Elevated copper levels suggest accelerated component wear and may indicate need for shortened service intervals or system inspection.
pH testing reveals brake fluid acidity that can cause internal corrosion within the ABS valve assembly. Acidic brake fluid accelerates component deterioration and may indicate contamination or excessive age requiring immediate replacement.
Protecting ABS Valve Assembly from Environmental Damage
Corrosion Prevention requires comprehensive protection strategies for vehicles operated in harsh environments. Road salt represents the most common cause of premature ABS valve assembly failure in northern climates. Regular undercarriage washing during winter months removes salt accumulation before it causes permanent damage.
Protective coatings applied to ABS valve assembly mounting areas and electrical connections provide long-term corrosion resistance. Professional undercoating services or corrosion inhibitor application can significantly extend component life in salt-exposed environments.
Drainage improvements around ABS valve assembly mounting locations help prevent water accumulation that accelerates corrosion. Blocked drain holes or damaged splash shields can trap moisture around valve assemblies, causing accelerated deterioration.
Temperature Extremes affect ABS valve assembly operation and longevity in several ways. Extreme cold can cause brake fluid viscosity changes that stress pump motors and affect system response time. Block heaters or garage storage help minimize cold-weather stress on ABS components.
High operating temperatures from aggressive driving or brake system problems can damage ABS valve assembly seals and electronic components. Proper brake system maintenance and avoiding excessive brake heating help protect valve assembly components from thermal damage.
Thermal cycling from extreme temperature variations causes expansion and contraction stress on valve assembly seals and housings. This stress accumulates over time and can cause premature seal failure or housing cracks requiring valve assembly replacement.
Road Debris Protection involves maintaining protective shields and splash guards that protect ABS valve assemblies from impact damage. Missing or damaged splash shields expose valve assemblies to road debris, salt spray, and impact damage that can cause premature failure.
Undercarriage inspection should include verification that all protective covers and shields are properly installed and in good condition. Damaged protection should be repaired promptly to prevent expensive valve assembly damage from environmental exposure.
Storage Considerations for vehicles in long-term storage require specific procedures to prevent ABS valve assembly damage during extended non-use periods. Brake fluid should be fresh before storage to prevent corrosion during storage periods. Battery maintenance or disconnection prevents uncontrolled system activation during storage.
Climate-controlled storage environments minimize temperature and humidity extremes that can damage ABS valve assembly components during extended storage. Moisture control is particularly important to prevent internal corrosion and electrical connection problems.
Periodic system activation during storage helps prevent component sticking and maintains proper operation. Monthly brief operation helps exercise solenoid valves and maintain seal flexibility, though this requires proper safety procedures and may not be practical for all storage situations.
Safety First: Critical Warnings for ABS Valve Assembly Work
Essential Safety Measures for ABS System Work
High-Pressure System Warnings must be understood by anyone working around ABS valve assemblies. These systems operate at pressures up to 2,000-3,000 PSI, which can cause serious injury if proper safety procedures are not followed. Brake fluid under high pressure can penetrate skin and cause serious internal injuries requiring immediate medical attention.
Depressurization procedures must be followed exactly before any ABS valve assembly service work. Most systems require specific procedures to safely relieve accumulator pressure and prevent accidental system activation. Never attempt to disconnect brake lines or electrical connections without proper system depressurization.
Eye protection is mandatory when working around ABS systems due to the risk of high-pressure brake fluid spray. Chemical-resistant safety glasses provide essential protection against brake fluid contact that can cause permanent eye damage. Face shields provide additional protection during high-risk procedures.
Brake System Criticality cannot be overstated when working on ABS valve assemblies. These components are directly responsible for vehicle stopping ability and occupant safety. Any work performed incorrectly can result in complete brake system failure, serious accidents, injuries, or death.
Life-safety implications of brake system work require careful consideration of skill level, available tools, and proper procedures before attempting any ABS valve assembly service. When in doubt about proper procedures or safety requirements, always seek professional assistance rather than risking safety.
Professional liability insurance and proper training are essential for anyone performing brake system service professionally. The potential consequences of brake system failure create significant liability exposure that requires proper insurance coverage and documented training.
Tool Safety requires proper selection, maintenance, and use of tools appropriate for ABS valve assembly service. Brake line wrenches must be the correct size and type to prevent fitting damage that can cause dangerous leaks. Improvised tools or incorrect sizes can cause expensive damage and safety hazards.
Hydraulic pressure testing equipment must be properly rated for brake system pressures and regularly calibrated for accuracy. Inadequate or damaged test equipment can provide false readings leading to improper diagnosis or unsafe conditions.
Lifting equipment must be adequate for safe vehicle access and properly positioned to prevent vehicle movement during service. ABS valve assemblies are typically located in areas requiring undercar access, making proper vehicle support essential for technician safety.
Personal Protective Equipment requirements for ABS valve assembly work include chemical-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and appropriate clothing. Brake fluid can cause skin irritation and damage painted surfaces, making proper protection essential during service procedures.
Respiratory protection may be required in poorly ventilated areas due to brake fluid vapors and cleaning solvents used during service. Proper ventilation is preferred over respiratory protection when possible, but both may be necessary in some service environments.
Work clothing should provide protection against brake fluid contact while allowing proper mobility for service procedures. Synthetic materials may be damaged by brake fluid contact, making natural fiber clothing preferable for brake system service.
Understanding Liability When Working on Critical Safety Systems
Professional Certification Requirements vary by jurisdiction but typically require specific training and certification for brake system service. ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification demonstrates professional competence in brake system service and repair. Some jurisdictions require specific licensing for brake system work due to safety implications.
Manufacturer certification programs provide specific training for particular ABS valve assembly designs and service procedures. This specialized training is often required for warranty work and provides detailed knowledge of system-specific requirements and procedures.
Continuing education requirements help ensure technicians remain current with evolving ABS technology and service procedures. Regular training updates are essential due to the rapid pace of ABS system development and changing service requirements.
Insurance Implications for brake system work include both professional liability coverage for service providers and potential coverage issues for vehicle owners performing DIY brake work. Professional technicians require adequate liability insurance covering brake system service due to the potential consequences of improper work.
Vehicle insurance coverage may be affected by improper brake system service or modification. Insurance companies may deny claims if brake system problems contribute to accidents and proper service procedures were not followed. Documentation of proper service and parts quality may be required for coverage.
Professional service provides liability protection for vehicle owners through technician insurance coverage and warranty protection. This protection may justify professional service costs for safety-critical brake system components like ABS valve assemblies.
Liability Limitations must be understood by anyone attempting brake system service. Personal liability for accidents caused by improper brake system service can be significant, including property damage, personal injury, and wrongful death claims. This liability exposure often exceeds the cost savings of DIY service.
Legal requirements for brake system service vary by jurisdiction and may require professional service for certain procedures or component replacements. Understanding local regulations helps ensure compliance and proper liability protection.
Documentation Requirements for brake system service include proper record-keeping of service procedures, parts used, and testing performed. This documentation provides legal protection and helps ensure proper service procedures were followed. Professional service typically includes comprehensive documentation not available with DIY service.
Service records should include component specifications, torque values, testing results, and any deviations from standard procedures. This documentation is essential for warranty claims, insurance coverage, and legal protection in case of problems.
Parts quality documentation, including part numbers, sources, and certifications, helps ensure proper component quality and provides legal protection. Using non-certified or inappropriate parts can create liability exposure and void warranties.
Recognizing the Limits of DIY ABS Valve Assembly Work
Complexity Indicators that suggest professional service is required include multiple diagnostic trouble codes, intermittent system operation, or symptoms affecting multiple brake system components. Complex problems often require professional diagnostic equipment and technical expertise beyond typical DIY capabilities.
Integration with other vehicle systems, such as traction control, stability control, or electronic brake distribution, increases complexity beyond typical DIY capabilities. These integrated systems require comprehensive understanding of system interactions and proper diagnostic procedures.
Manufacturer-specific procedures and special tools required for certain ABS valve assembly service may not be available to DIY enthusiasts. Professional service provides access to specialized tools and current technical information essential for proper service.
Safety Red Flags requiring immediate professional consultation include any brake pedal that travels to the floor, complete loss of brake pressure, or multiple brake system warning lights. These conditions indicate serious safety hazards requiring immediate professional attention.
Electrical problems affecting multiple systems or intermittent operation may indicate complex wiring or control module problems beyond DIY diagnostic capabilities. These problems require professional diagnostic equipment and expertise for safe resolution.
Equipment Limitations of typical DIY workshops include lack of proper hydraulic pressure testing equipment, ABS-capable scan tools, or specialized service tools required for safe ABS valve assembly service. Professional service provides access to equipment necessary for proper diagnosis and service.
Brake system bleeding equipment for ABS systems often requires pressure bleeding capabilities not available in typical DIY workshops. Improper bleeding procedures can result in brake system failure, making professional equipment access essential for safety.
Skill Assessment requires honest evaluation of technical knowledge, available tools, and safety understanding before attempting ABS valve assembly service. The safety-critical nature of brake systems requires conservative assessment of capabilities and willingness to seek professional help when needed.
Understanding of hydraulic systems, electrical diagnostics, and vehicle safety systems is essential for safe ABS valve assembly service. Lack of proper knowledge in any of these areas suggests professional service is the safer option.
For additional brake system safety information and professional service procedures, explore our comprehensive Brake System Resources for detailed safety guidance and technical information.
ABS Valve Assembly Replacement: Cost Planning and Budget Considerations
Understanding ABS Valve Assembly Pricing Variables
OEM vs. Aftermarket Options present significant cost and quality considerations for ABS valve assembly replacement. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) valve assemblies typically cost 25-50% more than aftermarket alternatives but provide guaranteed compatibility and often superior warranty coverage. OEM components ensure exact fit and function, reducing the risk of installation problems or premature failure.
Aftermarket valve assemblies vary significantly in quality, from budget options that may compromise reliability to premium aftermarket brands that meet or exceed OEM specifications. Quality aftermarket options can provide significant cost savings while maintaining proper performance and reliability. However, careful brand selection is essential to avoid inferior components that may fail prematurely.
Remanufactured valve assemblies offer a middle ground between new OEM and aftermarket options. Quality remanufactured units are rebuilt to OEM specifications using genuine parts where possible, often providing OEM performance at aftermarket prices. However, remanufactured components depend heavily on the quality of the rebuilding process and may have shorter warranty periods.
Warranty considerations significantly affect the long-term value of different component options. OEM components typically include comprehensive warranties that may extend to 3 years or 36,000 miles, while aftermarket options may have limited warranty coverage. The warranty value should be considered in total cost calculations, particularly for high-mileage vehicles.
Vehicle-Specific Factors dramatically influence ABS valve assembly pricing and availability. Luxury vehicles, European imports, and specialty applications often require expensive valve assemblies with limited aftermarket alternatives. Common domestic vehicle applications typically offer more pricing options and better parts availability.
Vehicle age affects both parts availability and pricing. Newer vehicles may have limited aftermarket options but good OEM availability, while older vehicles may have discontinued OEM parts but established aftermarket alternatives. Very old vehicles may have limited options in either category, potentially making valve assembly replacement impractical.
Production volume affects pricing significantly, with high-volume applications typically offering better pricing and availability. Low-production specialty vehicles may have extremely expensive valve assemblies with limited alternatives, making replacement cost a significant factor in repair decisions.
Regional Cost Variations reflect local market conditions, labor rates, and parts availability differences across geographic areas. Urban areas typically offer more competitive pricing due to higher competition among service providers, while rural areas may have limited options and higher pricing.
Parts availability varies regionally, particularly for specialty or imported vehicle applications. Some regions may have better access to remanufactured components or aftermarket alternatives, while others may depend primarily on OEM sources with higher pricing.
Shipping costs and delivery times for special-order components add to total replacement costs and may affect service scheduling. Rush shipping for urgent repairs can significantly increase total costs, making advance planning valuable for non-emergency replacements.
Core Exchange Programs can provide significant cost savings for ABS valve assembly replacement. Many suppliers offer remanufactured valve assemblies with core exchange, reducing costs by $200-500 compared to outright purchase. Core exchange requires returning the old valve assembly in rebuildable condition.
Core value depends on the condition of the original valve assembly and may be reduced or eliminated if the unit is not rebuildable. Severe damage, missing components, or excessive corrosion can reduce core value and increase total replacement costs.
Exchange programs typically require core return within a specific timeframe, often 30-90 days, to avoid core charges. Planning for core return during service scheduling helps ensure maximum cost savings from exchange programs.
Professional Service Investment Planning
Labor Time Estimates for ABS valve assembly replacement vary significantly based on vehicle design and component accessibility. Typical replacement times range from 2-6 hours, depending on the complexity of access and system bleeding requirements. Some applications may require significant component removal for valve assembly access, increasing labor time substantially.
Complex installations requiring computer programming, system calibration, or extensive disassembly can increase labor time to 8-12 hours for difficult applications. European luxury vehicles and some hybrid or electric vehicle applications may require extensive labor time due to system complexity.
System bleeding and testing procedures add to total labor time but are essential for safe operation. ABS system bleeding often requires special procedures and equipment that increase service time compared to conventional brake bleeding. Rushing these procedures to reduce costs can compromise safety and system reliability.
Shop Rate Variations reflect regional economic conditions, facility overhead, and technician skill levels. Independent repair facilities typically charge $80-120 per hour for brake system service, while dealership rates may range from $120-180 per hour. Specialty brake shops may offer competitive rates with specialized expertise.
Facility certification and equipment investment affect shop rates, with better-equipped facilities typically charging higher rates but providing superior service quality. Professional diagnostic equipment, proper lifting equipment, and technician training represent significant investments that justify higher service rates.
Geographic variations in shop rates reflect local economic conditions and cost of living differences. Urban areas typically have higher shop rates but more competitive pricing due to greater competition among service providers.
Additional Service Requirements often accompany ABS valve assembly replacement and should be included in total cost planning. Brake fluid replacement is mandatory with valve assembly replacement and adds $50-100 to total service costs. System bleeding may require special procedures adding 1-2 hours of labor time.
Related component inspection and potential replacement should be considered during valve assembly service. Brake hoses, master cylinder, and other hydraulic components may require attention during valve assembly replacement, particularly on high-mileage vehicles.
Computer programming or system calibration may be required after valve assembly replacement on some applications. These procedures require special equipment and technical knowledge, adding $100-200 to total service costs but ensuring proper system operation.
Warranty Considerations for professional service typically include parts and labor coverage for specified periods. Professional service warranties provide protection against defective components and improper installation, offering peace of mind for expensive brake system repairs.
Service warranty terms vary significantly between providers, from 30-day basic coverage to comprehensive warranties extending 12 months or 12,000 miles. Longer warranty periods provide better protection but may reflect higher service costs.
Warranty limitations and exclusions should be understood before authorizing service. Most warranties exclude damage from abuse, neglect, or related component failure, making proper system maintenance important for warranty protection.
Long-Term Financial Planning for ABS System Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance ROI demonstrates significant cost savings compared to emergency repairs or complete system replacement. Regular brake fluid service costing $75-150 annually can prevent valve assembly damage costing $1,500-3,000 to repair. The return on preventive maintenance investment is typically 10:1 or higher for brake system components.
Early problem detection through regular inspection and diagnostic testing can identify marginal components before complete failure occurs. Planned replacement allows better pricing research, parts sourcing, and service scheduling compared to emergency repairs that may require premium pricing for immediate service.
System-wide maintenance planning helps identify related components requiring attention before they cause expensive collateral damage. Maintaining proper brake fluid condition, replacing worn brake pads promptly, and addressing hydraulic leaks prevent damage to expensive ABS valve assemblies.
Failure Cost Implications extend beyond component replacement costs to include potential accident costs, towing expenses, and inconvenience factors. Emergency ABS valve assembly failure may require towing, emergency service rates, and rental car expenses that significantly exceed planned replacement costs.
Accident costs resulting from brake system failure can be catastrophic, including property damage, personal injury, and legal liability that far exceed any service cost savings. Insurance coverage may be compromised if proper maintenance was not performed, increasing personal liability exposure.
Safety Investment Perspective justifies professional service costs for critical brake system components like ABS valve assemblies. The safety benefits of properly functioning ABS systems far exceed service costs when considering accident prevention and occupant protection value.
Quality service and components provide long-term reliability that reduces total ownership costs compared to bargain service that may require repeat repairs. Professional service with proper warranties provides cost predictability and protection against unexpected expenses.
Resale Value Impact of proper brake system maintenance and documentation significantly affects vehicle value, particularly for safety-conscious buyers. Comprehensive service records demonstrating proper brake system maintenance can increase resale value and buyer confidence.
Deferred brake system maintenance creates liability concerns for sellers and may require disclosure of known problems. Addressing brake system maintenance before sale eliminates these concerns and may prevent buyer negotiations based on needed repairs.
Professional service documentation provides valuable proof of proper maintenance for warranty claims, insurance coverage, and resale value. This documentation often justifies the additional cost of professional service compared to DIY alternatives.
For comprehensive vehicle maintenance cost planning and professional service options, explore our Construction And Equipment resources for additional maintenance guidance applicable to various vehicle types.
Additional Resources for ABS Valve Assembly Service
Essential Service Information Sources
Vehicle Service Manuals provide the most comprehensive and accurate information for ABS valve assembly service procedures. OEM technical documentation includes component specifications, diagnostic procedures, special tool requirements, and safety warnings specific to each application. This information is essential for proper diagnosis and safe service procedures.
Professional service information databases, such as Mitchell OnDemand, AllData, or manufacturer-specific systems, provide current technical information including service bulletins, recalls, and updated procedures. These databases are regularly updated with new information and corrections not available in printed manuals.
Generic service information may not include critical details specific to particular ABS valve assembly designs. Manufacturer-specific information ensures proper procedures are followed and helps prevent expensive mistakes or safety hazards during service.
Wiring Diagrams are essential for electrical diagnosis of ABS valve assembly problems. These diagrams show circuit connections, component locations, connector pinouts, and signal characteristics necessary for proper electrical troubleshooting. Accurate wiring information prevents misdiagnosis and component damage during electrical testing.
Component location diagrams help technicians locate ABS valve assemblies, related components, and diagnostic connections. Many ABS valve assemblies are located in protected areas requiring specific access procedures outlined in service information.
Electrical system integration diagrams show relationships between ABS systems and related safety systems like traction control and stability management. Understanding these relationships is essential for comprehensive diagnosis of complex system problems.
Technical Service Bulletins document known problems, updated service procedures, and design improvements for specific ABS valve assembly applications. These bulletins often contain valuable diagnostic shortcuts and repair procedures not found in standard service manuals.
Recall information and safety campaigns may address ABS valve assembly problems with manufacturer-provided repairs or component updates. Checking for applicable recalls before performing service can save costs and ensure proper problem resolution.
Software updates and calibration procedures for ABS control modules may be necessary after valve assembly replacement. Technical bulletins document these requirements and provide proper procedures for system initialization.
Diagnostic Trouble Code References provide detailed information for interpreting ABS system error codes and developing proper diagnostic strategies. Generic code definitions may not provide sufficient detail for effective diagnosis, making manufacturer-specific code information essential.
Code setting conditions help technicians understand what system conditions trigger specific error codes and develop appropriate diagnostic procedures. This information prevents unnecessary component replacement and ensures accurate problem identification.
Related code information helps identify primary problems versus symptom codes that may be generated by other component failures. Understanding code relationships is essential for efficient diagnosis and proper repair procedures.
Finding Qualified ABS System Service Providers
Certification Requirements help identify technicians with proper training and expertise for ABS valve assembly service. ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification in brake systems (A5) demonstrates professional competence in brake system diagnosis and repair. Additional certifications in electrical systems (A6) and engine performance (A8) provide valuable expertise for complex ABS problems.
Manufacturer certification programs provide specialized training for specific ABS systems and service procedures. Technicians with manufacturer certifications have access to technical support, special tools, and warranty coverage not available to non-certified providers.
Professional organization membership, such as ASA (Automotive Service Association) or similar groups, indicates commitment to professional standards and continuing education. These organizations provide ongoing training and technical support for member technicians.
Equipment Standards necessary for proper ABS valve assembly service include professional diagnostic scan tools capable of ABS system communication, hydraulic pressure testing equipment, and proper brake bleeding equipment. Service providers should have equipment appropriate for the systems they service.
Diagnostic equipment should be regularly updated with current software and capable of accessing manufacturer-specific diagnostic procedures. Generic equipment may not provide sufficient diagnostic capability for complex ABS problems.
Safety equipment and proper facility design are essential for safe brake system service. This includes adequate ventilation, proper vehicle lifting equipment, and appropriate safety equipment for high-pressure hydraulic systems.
Service Quality Indicators include professional facility appearance, organized work areas, and evidence of ongoing training and certification. Quality service providers invest in proper facilities, equipment, and training that support superior service quality.
Customer testimonials and online reviews provide insight into service quality and customer satisfaction. Professional service providers typically have established reputations and positive customer feedback available through various sources.
Warranty policies and guarantee terms indicate confidence in service quality and provide protection for customers. Comprehensive warranties with reasonable terms suggest quality service and stand behind their work.
Service Guarantee Considerations should include both parts and labor coverage for reasonable periods. Quality service providers offer warranties that protect customers against defective components and improper installation while excluding damage from abuse or related component failure.
Warranty terms should be clearly explained before service authorization, including coverage limitations and customer responsibilities. Understanding warranty terms helps prevent disputes and ensures proper coverage when needed.
Follow-up service and customer support after warranty work demonstrates commitment to customer satisfaction and service quality. Professional service providers maintain customer relationships beyond initial service transactions.
ABS Valve Assembly Mastery: Your Path to Safer Braking
The ABS valve assembly represents one of the most sophisticated and safety-critical components in modern vehicles, requiring careful attention to maintenance, proper diagnosis, and professional service when problems arise. Understanding how these complex hydraulic and electronic assemblies function helps drivers recognize warning signs and make informed decisions about service needs.
Critical Safety Role of ABS valve assemblies cannot be overstated in modern vehicle safety systems. These components prevent wheel lockup during emergency braking, maintain steering control, and integrate with advanced safety systems like electronic stability control and traction management. When ABS valve assemblies function properly, they can mean the difference between a controlled stop and a dangerous accident.
The sophisticated technology within ABS valve assemblies requires respect for their complexity and recognition of their safety-critical role. Split-second pressure modulation at individual wheels requires precision hydraulic and electronic components working in perfect harmony. Any compromise in this system affects not only stopping performance but also the operation of related safety systems.
Diagnostic Importance in preventing unnecessary component replacement and ensuring accurate problem identification cannot be overlooked. ABS valve assembly symptoms can mimic other brake system problems, making proper diagnostic procedures essential for cost-effective repairs. Professional diagnosis with appropriate equipment often reveals less expensive solutions than complete valve assembly replacement.
Systematic diagnostic approaches help identify specific component failures within valve assemblies, potentially allowing targeted repairs rather than complete replacement. However, the complexity of these systems and their safety-critical role often favor replacement over repair attempts for long-term reliability.
Professional Guidance becomes essential when dealing with the high-pressure hydraulic systems, complex electronics, and safety-critical nature of ABS valve assemblies. While basic maintenance and inspection are appropriate for skilled DIY enthusiasts, diagnosis and replacement require professional expertise, specialized equipment, and comprehensive safety procedures.
Professional technicians provide liability protection, warranty coverage, and access to manufacturer-specific service information essential for proper ABS valve assembly service. The potential consequences of improper brake system service far exceed any cost savings from DIY attempts on these critical components.
Maintenance Value through preventive care extends component life, ensures reliable operation, and prevents expensive emergency repairs. Regular brake fluid service represents the most cost-effective maintenance for ABS valve assemblies, preventing contamination and corrosion that cause premature failure.
Early recognition of warning signs and prompt professional evaluation can often prevent complete valve assembly failure. Dashboard warning lights, changes in brake pedal feel, or unusual sounds during braking deserve immediate attention to prevent safety hazards and expensive repairs.
Safety Priority must always take precedence over cost considerations when dealing with brake system components. ABS valve assemblies directly affect occupant safety and vehicle control during emergency situations when proper brake function is most critical. Compromising on service quality, component quality, or proper procedures creates unacceptable safety risks.
Professional service with proper warranties provides peace of mind and protection against component failure when it matters most. The investment in quality service and components provides safety assurance that cannot be quantified in cost comparisons alone.
Action Steps for Readers
Immediate Actions for ABS valve assembly care include visual inspection of external components, electrical connections, and brake fluid level monitoring. Monthly visual checks can identify developing problems before they cause complete system failure or safety hazards.
Check dashboard warning lights and have any ABS-related warnings evaluated professionally immediately. Ignoring warning signs allows minor problems to develop into expensive major failures that compromise vehicle safety.
Planning Considerations for potential ABS valve assembly service should include budget development for both routine maintenance and potential component replacement. Understanding typical service costs helps in financial planning and prevents deferred maintenance that can cause safety problems.
Research qualified service providers in your area before problems occur, focusing on facilities with proper certification, equipment, and warranty coverage. Establishing relationships with quality service providers ensures access to professional help when needed.
Professional Consultation should be sought immediately for any symptoms suggesting ABS valve assembly problems. Qualified technicians can provide accurate diagnosis, service recommendations, and safety guidance tailored to specific vehicle applications and operating conditions.
Don’t attempt diagnosis or repair of ABS valve assemblies without proper training, equipment, and safety procedures. The complexity and safety-critical nature of these systems require professional expertise for safe and effective service.
Maintenance Scheduling should prioritize brake fluid service at manufacturer-recommended intervals and include regular professional inspection of ABS system operation. Preventive maintenance provides the best protection against expensive failures and ensures optimal safety system performance.
Document all brake system service and maintain records for warranty coverage, resale value, and service planning. Comprehensive maintenance records demonstrate proper care and help ensure continued system reliability.
For additional technical resources and professional service support for your specific vehicle, explore our comprehensive ABS Control Module: The Brains Behind Your Safe Stops guide and professional Service Manual collection for detailed technical information and service procedures.
Remember: Your ABS valve assembly is working every time you brake, even when you don’t feel it operating. Proper maintenance and professional service ensure this critical safety system is ready when you need it most. When in doubt about any brake system concern, prioritize safety and seek professional evaluation immediately.
About Repairs Advisor: We provide comprehensive technical information and professional-grade service manuals to help you understand, maintain, and repair your vehicles and equipment. Our experienced team of technicians ensures accurate, safety-focused content for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
Need Professional Help? If you’re experiencing ABS valve assembly problems or need technical support, contact our expert team at [email protected] or visit our Help Center for comprehensive technical support.
Disclaimer: This information is provided for educational purposes only. ABS valve assembly service involves safety-critical brake system components. Always consult qualified professional technicians for diagnosis, repair, and replacement of brake system components. Improper brake system service can result in brake failure, accidents, injury, or death. Repairs Advisor assumes no liability for actions taken based on this information.
