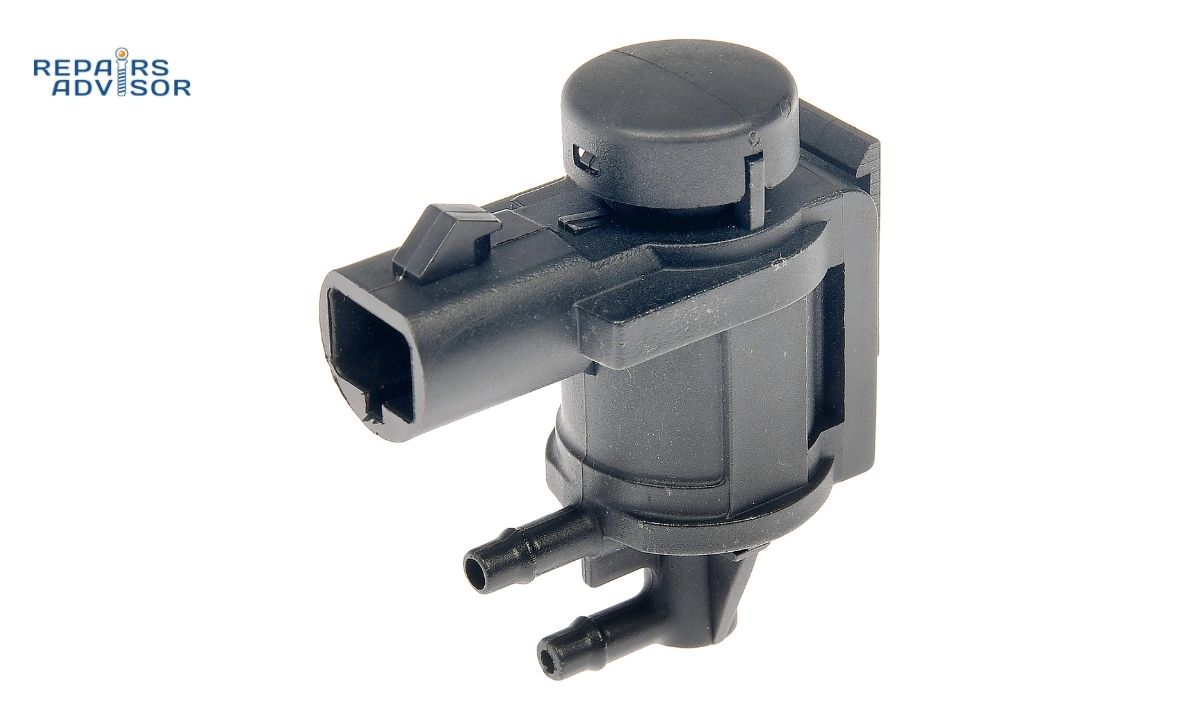
Within your vehicle’s Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, the EGR vacuum solenoid acts as a crucial electronic valve. Its primary role is to precisely control and distribute engine vacuum to the EGR valve when commanded by the engine control module (ECM). This controlled vacuum allows the ECM to open and close the EGR valve, precisely regulating the flow of exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chambers. This recirculation helps lower combustion temperatures, which significantly reduces the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) and prevents engine “pinging” or detonation. When this solenoid malfunctions, it can disrupt the precise operation of the EGR system, leading to various performance and emissions issues.
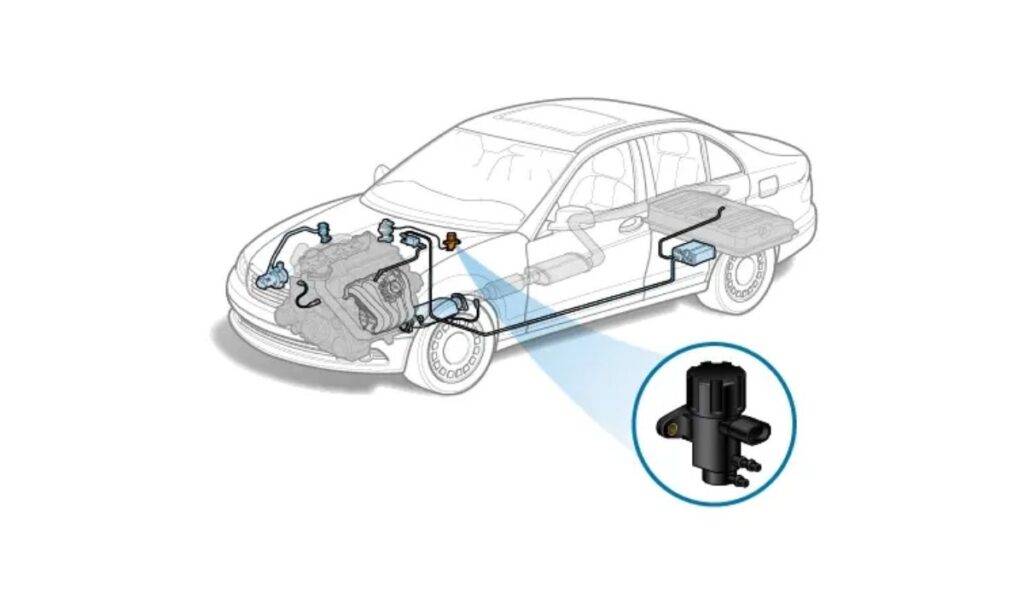
Key Indicators Your EGR Vacuum Solenoid Might Be Failing
When the EGR vacuum solenoid experiences a malfunction, your vehicle will often provide clear feedback through warning lights and noticeable changes in engine behavior:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light (CEL):
- This is the most common and often the first indicator. If the EGR vacuum solenoid fails to open or close as commanded by the ECM, or if its electrical circuit develops an issue, the ECM will detect a fault. This will cause the Check Engine Light to illuminate on your dashboard.
- You’ll likely see specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the EGR system, such as codes indicating EGR flow problems (e.g., P0400, P0401, P0402) or circuit malfunctions specific to the solenoid (e.g., P0403 – EGR Control Circuit Malfunction).
- Engine “Pinging” or Knocking During Acceleration:
- The EGR system is designed to introduce exhaust gases to lower combustion temperatures, preventing premature ignition (pre-ignition or detonation), which manifests as “pinging” or knocking. If the EGR vacuum solenoid is faulty, it might not allow the EGR valve to open, or to open sufficiently.
- This failure to recirculate exhaust gases leads to higher combustion temperatures, especially during acceleration. The result is a distinct “pinging” or “knocking” sound from the engine, indicating uncontrolled combustion. This is a serious symptom that can lead to significant engine damage over time.
- Emissions Test Failure:
- A properly functioning EGR system is crucial for reducing NOx emissions. If the EGR vacuum solenoid prevents the EGR valve from operating correctly, the engine will produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides.
- Consequently, your vehicle will likely fail an emissions inspection or smog test in areas with strict environmental regulations.
- Rough Idle or Stalling (Less Common, Indirect):
- While primarily affecting the engine under load, a faulty EGR vacuum solenoid that causes the EGR valve to stick open or partially open at idle can lead to a rough or erratic engine idle, or even stalling, as it introduces exhaust gases when they’re not needed.
How to Address a Failing EGR Vacuum Solenoid
Repairing a faulty EGR vacuum solenoid involves a precise diagnostic process to confirm the solenoid itself is the issue, followed by its replacement, and a thorough inspection of related components.
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Procedures Are Essential:
- Scan for Codes: Begin by using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored diagnostic trouble codes. Codes specifically related to EGR flow or solenoid circuit issues are key indicators.
- Live Data Monitoring: A professional technician will use a scan tool to monitor “live data” related to the EGR system, including the commanded state of the EGR vacuum solenoid and the actual EGR valve position (if available). This helps determine if the solenoid is receiving commands and responding.
- Functional Tests: Many advanced scan tools allow technicians to perform “bidirectional control” tests, where they can command the EGR vacuum solenoid to activate. The technician will listen for an audible click from the solenoid and observe if it produces vacuum or controls the EGR valve as expected.
- Vacuum Line Inspection: It is critical that all related vacuum hoses are thoroughly inspected whenever the EGR vacuum solenoid is replaced or suspected of failure. Cracks, leaks, or blockages in the vacuum lines can prevent the solenoid from delivering vacuum to the EGR valve, mimicking a faulty solenoid.
- Electrical Circuit Check: The technician will check the electrical connector and wiring to the solenoid for proper power, ground, and signal integrity.
- EGR Valve Condition Check: While diagnosing the solenoid, the proper operation of the EGR valve itself should also be confirmed. A sticky, clogged, or faulty EGR valve can prevent proper EGR flow even if the solenoid is working correctly.
- Replacement of the EGR Vacuum Solenoid:
- Once the EGR vacuum solenoid is definitively confirmed as the faulty component (and not a vacuum leak or an issue with the EGR valve), it must be replaced.
- The replacement process typically involves disconnecting the electrical connector and any vacuum lines, then unbolting or unmounting the old solenoid from its location.
- A new, OEM-quality replacement solenoid is then installed, ensuring all connections are secure.
- Address Related Issues (If Any):
- If any vacuum hoses were found to be cracked or leaking during the inspection, they should be replaced.
- If the EGR valve or its passages were found to be clogged with carbon buildup, they should be cleaned or replaced to ensure the entire EGR system functions optimally.
- If the engine was “pinging,” resolving the EGR issue should eliminate this potentially damaging problem.
- Clear Codes and Verify Repair:
- After the new solenoid is installed and any related issues are addressed, the technician will clear the stored diagnostic trouble codes from the vehicle’s computer.
- A final verification step often involves a test drive, monitoring live data from the EGR system, and ensuring that the Check Engine Light does not return and that the engine performs smoothly without any “pinging” or knocking. The vehicle should then be able to pass emissions testing.
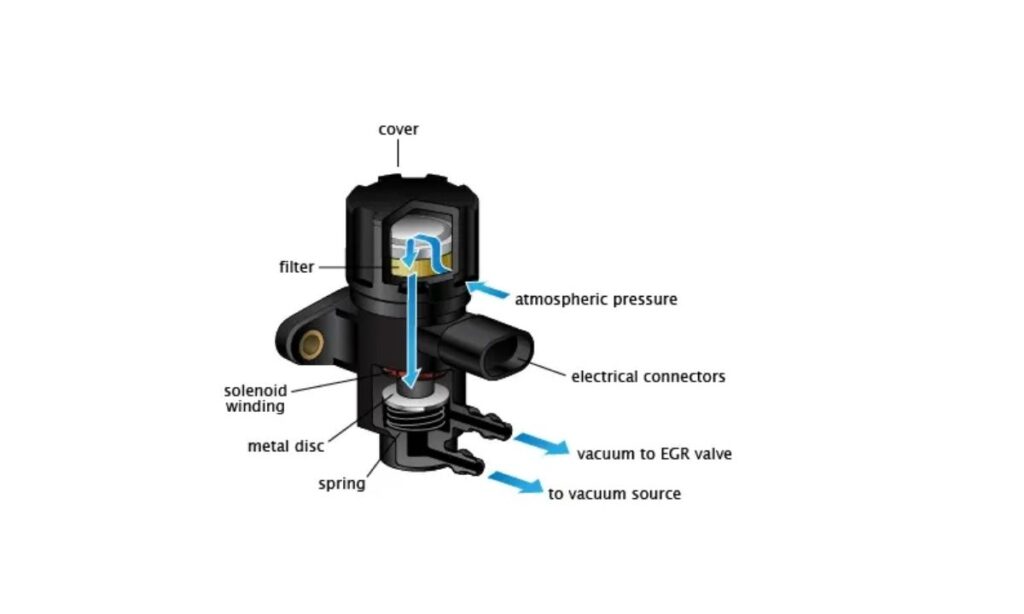
Your Repair Advisor’s Take:
The EGR vacuum solenoid is a seemingly small component, but it plays a significant role in your vehicle’s ability to control emissions and prevent damaging engine “pinging.” A faulty solenoid can lead to persistent Check Engine Lights, compromised engine performance, and failed emissions tests. Given the interconnectedness of the EGR system, a thorough diagnostic is crucial to avoid misdiagnosis.
Don’t ignore the warning signs of a bad EGR vacuum solenoid, especially engine “pinging,” which can cause severe, long-term damage. Simply replacing parts without confirming the root cause can be a costly and ineffective solution.
For accurate diagnosis and effective repair of your EGR system, always consult a qualified automotive technician. They have the specialized tools, knowledge, and experience to pinpoint whether the solenoid, vacuum hoses, the EGR valve itself, or another component is the true culprit. Ensure your engine runs efficiently, cleanly, and safely – schedule a professional EGR system diagnostic today!
