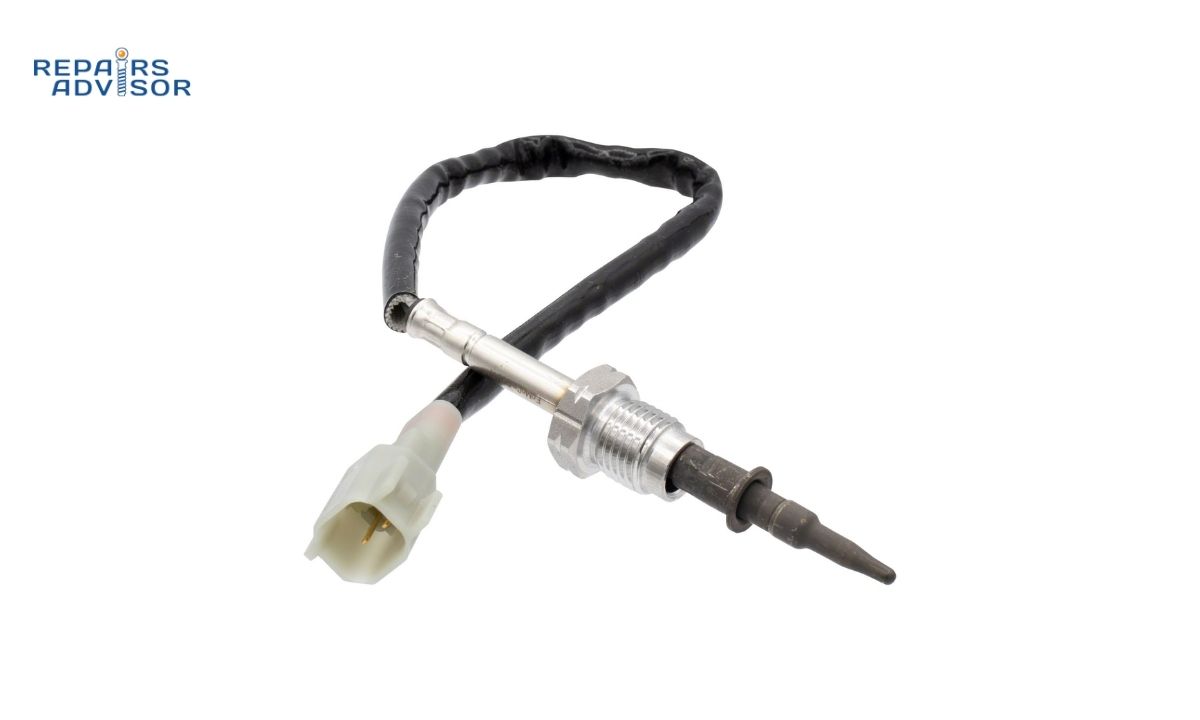
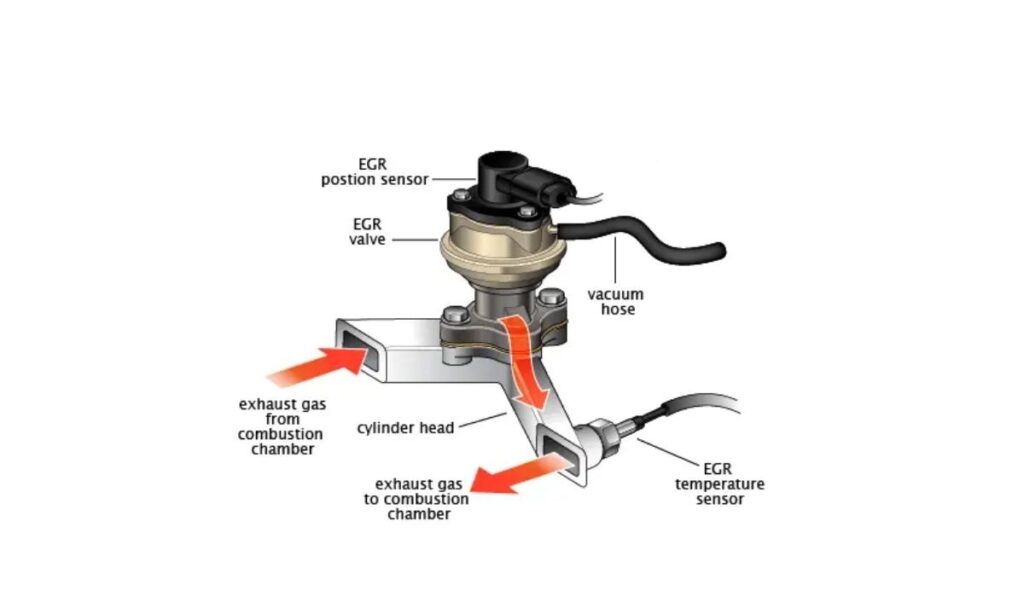
Within your vehicle’s Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, the EGR temperature sensor acts as a crucial electrical sensing probe. Its vital role is to monitor the temperature of the exhaust gases as they are recirculated back into the engine. This sensor then precisely transmits this temperature data to the engine control computer (ECM). The ECM uses this information to verify the proper operation of the EGR system, ensuring that the exhaust gases are indeed flowing and at the correct temperature for effective emissions reduction and engine performance.
When this sensor malfunctions, it can disrupt the delicate balance of the EGR system, leading to various issues.
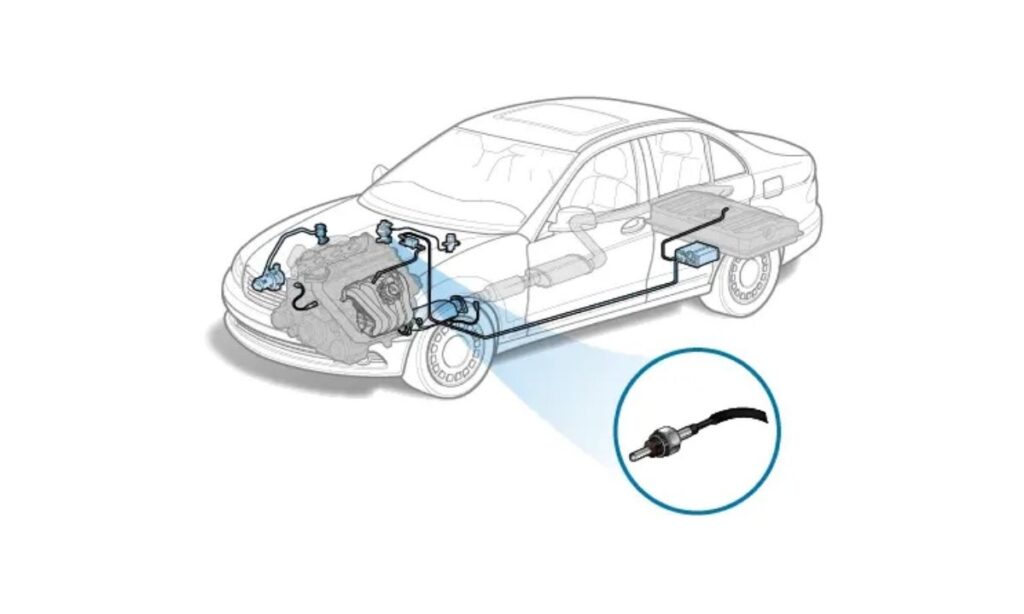
Symptoms of a Bad or Failing EGR Temperature Sensor
Problems with an EGR temperature sensor can trigger warning lights, affect engine combustion, and lead to emissions issues:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination:
- This is the most common and often the first indicator. If the EGR temperature sensor sends an implausible signal (too high, too low, or no signal at all), or if its readings don’t match the ECM’s expected parameters for EGR operation, the ECM will detect a fault and illuminate the Check Engine Light on your dashboard.
- You’ll likely see specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the EGR temperature sensor circuit or performance (e.g., P0405 – EGR Sensor A Circuit Low, P0406 – EGR Sensor A Circuit High, or codes related to EGR temperature rationality).
- Engine “Pinging” or Knocking on Acceleration:
- The primary function of the EGR system is to lower combustion temperatures, which prevents the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) and also helps prevent “pinging” or engine knock. If the EGR temperature sensor is faulty and providing incorrect information, the ECM might not command the EGR valve to open effectively.
- This can lead to higher-than-normal combustion temperatures, especially during acceleration, resulting in a distinct “pinging” or “knocking” sound from the engine. This sound indicates pre-ignition or detonation and can lead to serious engine damage over time if not addressed.
- Emissions Failure:
- Since the EGR system (and its temperature sensor) is critical for controlling NOx emissions, a faulty sensor can lead to the system not operating correctly. This often results in increased levels of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust.
- Consequently, your vehicle will likely fail an emissions inspection or smog test in areas with regulations.
- Rough Idle or Stalling (Less Common, Indirect):
- While less direct, an inaccurate EGR temperature sensor can indirectly affect engine idle. If the ECM receives bad data, it might mismanage the EGR flow, potentially causing the engine to run slightly rough or even stall in some conditions, especially at low RPMs.
How to Fix a Bad EGR Temperature Sensor
Repairing a bad EGR temperature sensor typically involves proper diagnosis to confirm the sensor itself is the issue, followed by its replacement.
- Thorough Diagnostic is Essential:
- Scan for Codes: Start by using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored diagnostic trouble codes. Codes specifically referencing the EGR temperature sensor circuit or performance are strong indicators.
- Live Data Monitoring: A professional mechanic will use a scan tool to monitor “live data” from the EGR temperature sensor. They’ll observe the sensor’s readings and compare them to expected values for different engine temperatures and EGR valve positions. They might also monitor other related sensors to see if the temperature readings are plausible.
- Wiring and Connector Inspection: The mechanic will visually inspect the electrical connector and wiring leading to the EGR temperature sensor for any signs of corrosion, damage, or loose connections. These can often mimic a bad sensor.
- EGR Valve Check: It is crucial that the EGR valve itself is checked for proper operation whenever the EGR temperature sensor is replaced or suspected of failure. A stuck or faulty EGR valve can directly impact exhaust gas temperatures and flow, potentially leading to misleading sensor readings or even damaging the new sensor. The mechanic will check if the EGR valve opens and closes smoothly and if its passages are clear of carbon buildup.
- Replacement of the EGR Temperature Sensor:
- Once the EGR temperature sensor is confirmed as the faulty component (and not a symptom of a larger EGR system issue), it must be replaced.
- The replacement process involves disconnecting the electrical connector and carefully unthreading or unbolting the old sensor from its mounting location (often on the EGR valve or exhaust manifold).
- A new, OEM-quality replacement sensor is then installed, ensuring proper torque and connection.
- Address Related Issues (If Any):
- If the EGR valve or its passages were found to be clogged with carbon during diagnosis, these should be cleaned or replaced as necessary to ensure the entire EGR system functions optimally.
- If the engine was “pinging,” resolving the EGR issue should eliminate this potentially damaging problem.
- Clear Codes and Verify Repair:
- After the new sensor is installed and any related issues are addressed, the mechanic will clear the stored diagnostic trouble codes from the vehicle’s computer.
- A final verification step often involves a test drive, monitoring live data, and ensuring that the Check Engine Light does not return and that the engine performs smoothly without any “pinging” or knocking. The vehicle should then be able to pass emissions testing.
Conclusion
The EGR temperature sensor is a small but critical component that helps your vehicle manage emissions and prevent harmful engine knock. A malfunctioning sensor can trigger that unwelcome Check Engine Light, lead to potentially damaging engine “pinging,” and cause your vehicle to fail emissions tests. While the sensor itself might be the issue, it’s part of a larger, interconnected EGR system that requires a holistic approach to diagnosis.
Don’t ignore the warning signs of a bad EGR temperature sensor, especially engine “pinging” which can cause severe damage. Simply replacing the sensor without a thorough diagnostic can lead to recurring problems if the underlying issue lies elsewhere in the EGR system.
For accurate diagnosis and effective repair of your EGR system, always consult a qualified automotive technician. They have the specialized tools and expertise to pinpoint whether the sensor, the EGR valve, or another component is the true culprit, ensuring your engine runs efficiently, cleanly, and safely. Protect your engine and the environment – schedule a professional EGR system diagnostic today!
