A malfunctioning door window motor can quickly transform a minor inconvenience into a serious safety and security concern. Whether your power windows are operating slowly, making unusual noises, or have stopped working entirely, understanding the underlying causes and solutions is essential for every vehicle owner.
The door window motor, also known as a power window motor, serves as the heart of your vehicle’s power window system. This critical electrical component works in conjunction with the window regulator to provide smooth, controlled movement of your vehicle’s windows. When functioning properly, it operates silently and efficiently, but when problems arise, the symptoms are typically unmistakable.
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electrical systems, and the power window motor represents one of the most frequently used components in daily driving. From adjusting ventilation to ensuring security, properly functioning windows are essential for both comfort and safety. Understanding how to diagnose problems early can save you from costly repairs and potential security vulnerabilities.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about door window motors, from basic operation principles to professional diagnosis procedures. Safety remains our top priority throughout this technical discussion, as electrical automotive work requires proper precautions and professional expertise when complexity exceeds DIY capabilities.
Whether you’re a professional mechanic, DIY enthusiast, or simply want to understand your vehicle better, this guide provides the technical knowledge and practical insights needed to make informed decisions about window motor maintenance and repair.
What is a Door Window Motor?
Basic Function and Purpose
The door window motor functions as the primary power source for your vehicle’s electric window system. This specialized electrical component converts 12-volt DC power from your vehicle’s electrical system into controlled mechanical motion, enabling precise window positioning and smooth operation.
The motor’s primary role involves receiving electrical signals from the window control switches and translating those commands into rotational force. Unlike standard electric motors, window motors incorporate specific gear ratios and torque characteristics designed to handle the weight and resistance of automotive glass panels safely and efficiently.
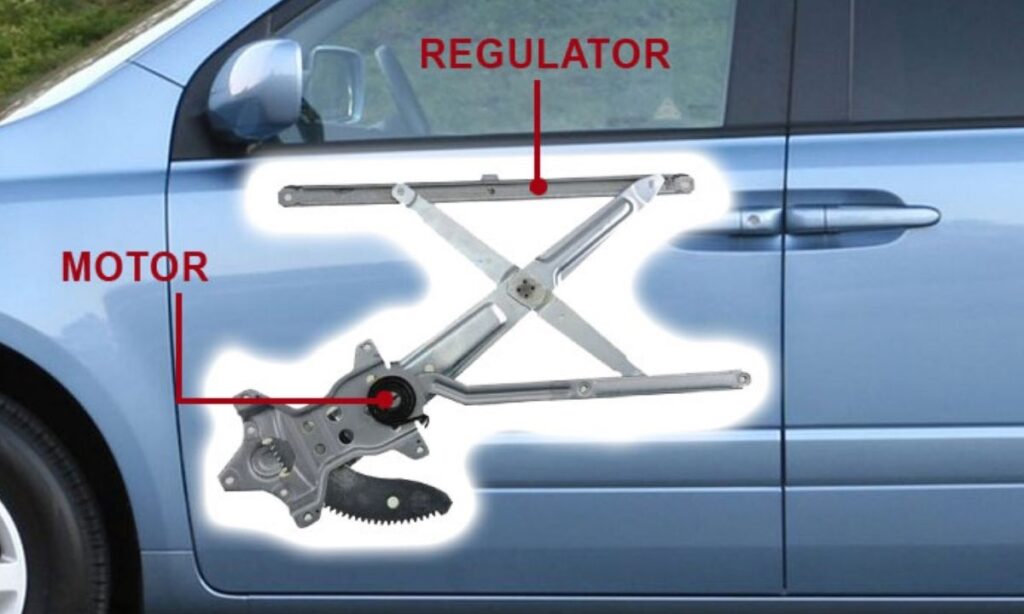
Integration with the window regulator system creates a complete mechanical assembly. The motor provides rotational power, while the regulator mechanism converts that rotation into linear motion, guiding the window glass along predetermined tracks. This partnership ensures controlled movement and prevents glass damage during operation.
Modern vehicles typically employ different motor configurations depending on the specific window system design. Single motor systems control one window per motor, while some advanced configurations may incorporate dual motor arrangements for enhanced precision or backup functionality in luxury applications.
Understanding your vehicle’s electrical system capacity is crucial when diagnosing motor problems. Power window motors draw significant current during operation, and electrical system health directly impacts motor performance and longevity.
Components and Assembly
The door window motor assembly consists of several critical components working in precise coordination. The motor housing protects internal electrical components while providing mounting points for secure installation within the door panel structure.
Internal components include the electric motor itself, featuring permanent magnets, armature windings, and carbon brushes that create the electromagnetic fields necessary for rotation. Professional-grade window motors incorporate thermal protection to prevent damage from excessive heat buildup during heavy use or electrical problems.
The gear reduction system represents a crucial element in motor functionality. High-ratio gears reduce motor speed while increasing torque output, providing the mechanical advantage necessary to move heavy glass panels against wind resistance and track friction. Quality gears ensure long-term reliability and smooth operation.
Mounting brackets and attachment points require precise engineering to handle the operational stresses and vibrations inherent in automotive applications. These components must maintain alignment while accommodating thermal expansion and road-induced movement.
Wiring harnesses connect the motor to the vehicle’s electrical system through specialized connectors designed for automotive environments. These connections must resist moisture, corrosion, and mechanical stress while maintaining reliable electrical contact throughout the motor’s service life.
Safety features and limit switches prevent motor damage and ensure operator protection. Modern window motors incorporate overcurrent protection and position sensing to prevent glass damage and motor burnout during obstructions or mechanical binding.
How Door Window Motors Work
The operational sequence begins when the driver or passenger activates a window control switch. This action sends a specific voltage signal through the vehicle’s electrical system to the appropriate door window motor, initiating the movement cycle.
Upon receiving the electrical signal, the motor’s internal electromagnets create rotating magnetic fields that cause the armature to spin in the desired direction. The direction of rotation depends on the polarity of the applied voltage, controlled by the window switch position.
The motor’s high-speed rotation passes through the integrated gear reduction system, which significantly reduces rotational speed while proportionally increasing torque output. This mechanical advantage enables the motor to move heavy glass panels against various resistance forces.
Mechanical transfer to the window regulator occurs through a drive mechanism that converts the motor’s rotational output into linear motion. The regulator’s mechanical linkages guide the window glass along predetermined tracks, ensuring smooth vertical movement without binding or misalignment.
Up and down operation cycles involve precise timing and control to prevent damage to the glass, motor, or regulator components. Quality window motors incorporate feedback systems that monitor position and load, automatically adjusting operation parameters for optimal performance.
Integration with the vehicle’s electrical system requires proper voltage regulation and current management. For comprehensive understanding of automotive electrical systems, refer to our detailed guide on Understanding Your Vehicle’s Electrical and Lights Systems.
Common Door Window Motor Problems
Motor Burnout and Electrical Failure
Motor burnout represents one of the most serious and common door window motor failures. This condition typically results from prolonged overload situations, where the motor attempts to operate against excessive resistance or obstruction. When motors work beyond their designed capacity, internal components overheat and eventually fail permanently.
Electrical overload can occur when window glass becomes stuck due to ice, debris, or mechanical binding in the regulator tracks. Continued attempts to operate the window under these conditions force the motor to draw excessive current, leading to overheating and component failure.
Age-related deterioration affects motor performance as internal components wear and electrical resistance increases. Carbon brushes wear down over time, reducing electrical contact efficiency and increasing heat generation. Motor windings can develop insulation breakdown, creating short circuits and electrical failures.
Moisture intrusion poses a significant threat to electrical components within door panels. Water entry through damaged door seals, window weatherstripping, or drainage system failures can cause corrosion and electrical shorts. Even small amounts of moisture can create serious electrical problems in sensitive motor components.
Control module and switch failures often mimic motor problems, making accurate diagnosis essential. Modern vehicles incorporate sophisticated window control modules that manage multiple motors and safety features. When these electronic components fail, symptoms may appear identical to motor burnout.
Intermittent electrical connections create frustrating and unpredictable window operation. Loose connections, corroded terminals, or damaged wiring can cause sporadic motor function that worsens over time. These electrical issues often start as minor inconveniences but can progress to complete system failure if left unaddressed.
Understanding your vehicle’s Car’s Fuse Box: All Things You Should Know helps identify electrical issues that may affect window motor operation.
Mechanical Wear and Damage
Gear wear represents a gradual but inevitable process in window motor operation. The constant cyclic loading and unloading of gear teeth during window operation causes microscopic wear that accumulates over thousands of cycles. Quality motors incorporate hardened gears designed for extended service life, but eventual replacement becomes necessary.
Stripped gear teeth occur when excessive torque loads exceed the mechanical limits of the gear system. This can happen during attempts to operate windows against obstructions, during freezing conditions, or when other mechanical components bind or fail. Once gear teeth strip, motor replacement becomes the only viable repair option.
Bearing failure affects motor smoothness and can lead to complete mechanical seizure. Internal motor bearings support the rotating armature and must operate reliably under varying temperature and load conditions. Bearing noise often provides early warning of impending failure, allowing for proactive replacement before complete breakdown.
Motor shaft problems include wear, corrosion, or mechanical damage that affects the connection between the motor and regulator system. The output shaft must maintain precise alignment and smooth rotation to ensure proper window operation and prevent premature wear of connected components.
Mounting bracket stress occurs due to the operational forces and vibrations inherent in automotive applications. Repeated loading cycles can cause fatigue failures in mounting hardware, leading to motor misalignment and operational problems. Quality installation and proper torque specifications help prevent these issues.
Foreign object damage can occur when debris enters the door panel space and interferes with motor operation. Small objects, broken glass fragments, or accumulated dirt can cause binding and force the motor to work against abnormal resistance, leading to premature failure.
Environmental Factors
Moisture intrusion represents perhaps the most serious environmental threat to door window motor longevity. Water entry through compromised door seals creates ideal conditions for corrosion and electrical component degradation. Even small amounts of moisture can cause significant problems in electrical systems.
Temperature effects influence motor performance across the operational range typical in automotive applications. Extreme cold can cause lubricants to thicken, increasing operational resistance and motor load. High temperatures accelerate component aging and can cause thermal damage to electrical insulation and plastic components.
Road salt and chemical exposure create corrosive conditions that attack metal components and electrical connections. Winter road treatments and industrial environments pose particular challenges for automotive electrical systems. Regular cleaning and protection help mitigate these environmental threats.
UV degradation affects plastic components and wire insulation over time. Extended exposure to sunlight can cause brittleness and cracking in polymer materials, leading to water intrusion and mechanical failures. Quality automotive components incorporate UV stabilizers to resist this degradation.
Understanding how environmental factors affect your vehicle’s electrical system helps in preventive maintenance planning. Proper drainage system maintenance and seal inspection can prevent many moisture-related failures before they occur.
Signs of a Bad Door Window Motor
Early Warning Signs
Slow window operation often represents the first noticeable symptom of motor deterioration. When a window that previously moved quickly begins operating sluggishly, internal motor wear or electrical resistance has likely increased beyond normal parameters. This gradual degradation allows time for planned replacement before complete failure.
Intermittent function creates unpredictable window behavior that can range from minor inconvenience to serious safety concerns. The window may work normally sometimes but fail to respond to switch commands at other times. This symptom often indicates electrical connection problems, worn motor brushes, or developing control system issues.
Unusual sounds during operation provide valuable diagnostic information about the nature and severity of motor problems. Grinding, squealing, or clicking noises typically indicate mechanical wear or damage within the motor or connected regulator system. Different sounds often point to specific component failures.
Window stopping mid-travel represents a more advanced symptom that suggests significant motor or regulator problems. The motor may lack sufficient power to complete the full range of motion, or mechanical binding may prevent normal operation. This condition requires immediate attention to prevent further damage.
Temperature sensitivity can indicate electrical problems or motor overheating issues. Windows that work properly in cool conditions but fail during hot weather often have electrical resistance or thermal protection problems requiring professional diagnosis.
Irregular window speed during operation suggests gear wear or electrical supply problems. Normal window operation should maintain consistent speed throughout the travel range, with variations indicating internal component deterioration.
For comprehensive information about related electrical system problems, explore our guide on Signs of a Bad or Failing Alternator, as charging system issues can affect window motor performance.
Advanced Symptoms
Complete motor failure represents the most obvious and problematic symptom, where the window becomes completely unresponsive to switch commands. No sound or movement occurs when attempting window operation, indicating total motor breakdown or complete electrical failure. This condition requires immediate professional attention.
Window stuck in up or down position creates serious practical and safety implications. A window stuck in the down position compromises vehicle security and weather protection, while a window stuck up can create emergency exit problems and ventilation issues. Both conditions require urgent repair consideration.
Burning smell from door panel indicates serious electrical problems that pose potential safety hazards. The characteristic odor of overheated electrical components suggests immediate system shutdown and professional inspection. Continued operation under these conditions can lead to electrical fires.
Blown fuses or electrical issues affecting window operation often indicate motor overload or electrical short circuits. Repeatedly blown window fuses suggest excessive current draw typically caused by motor problems or electrical shorts. This condition requires systematic electrical diagnosis.
Multiple window failures simultaneously usually point to control system problems rather than individual motor issues. Central control modules, main electrical supply problems, or body control system failures can affect multiple windows simultaneously.
Physical evidence of component failure may include visible damage to motor mounting, abnormal door panel bulging, or mechanical interference sounds during door operation. These symptoms often indicate catastrophic component failure requiring comprehensive repair.
Diagnostic Indicators
Testing window switch operation helps isolate electrical control problems from motor issues. Switch testing should include checking all positions and verifying proper electrical continuity through the control circuits. Faulty switches can mimic motor problems and lead to unnecessary component replacement.
Checking electrical connections involves systematic verification of voltage supply, ground connections, and signal continuity throughout the window control system. Proper electrical diagnosis requires understanding of automotive electrical principles and appropriate testing equipment.
Listening for motor activation sounds provides valuable diagnostic information even when window movement doesn’t occur. A motor that attempts to run but fails to move the window indicates mechanical binding or regulator problems rather than electrical motor failure.
Visual inspection of window movement can reveal mechanical alignment problems, binding conditions, or regulator component failures. Uneven or jerky window motion typically indicates mechanical rather than electrical problems.
Professional diagnostic equipment enables precise measurement of motor current draw, voltage supply, and operational parameters that confirm motor condition and identify specific failure modes.
Load testing procedures help determine motor capacity and identify developing problems before complete failure occurs. These tests require specialized equipment and expertise but provide definitive motor condition assessment.
Safety Concerns
Security risks with non-functioning windows create serious practical and safety implications for vehicle owners. Windows stuck in the down position compromise vehicle security, making theft and unauthorized access significantly easier. This condition requires prompt repair for personal safety and property protection.
Weather protection issues affect both comfort and safety, particularly during adverse weather conditions. Non-functioning windows can allow rain, snow, or extreme temperatures to affect the vehicle interior and occupant comfort. Emergency weather situations make functioning windows essential for safety.
Emergency exit considerations become critical in accident situations where normal door operation may be compromised. Vehicle occupants may need to exit through windows during emergency situations, making reliable window operation a safety requirement rather than mere convenience.
Impact on vehicle ventilation affects both comfort and safety, particularly in hot climates where interior temperature control becomes essential for health and safety. Proper ventilation helps prevent heat-related health issues and maintains safe driving conditions.
Understanding related electrical system safety is crucial for comprehensive vehicle safety. Our detailed information about Why Your Car Battery Dies, and What to Do About It helps maintain overall electrical system health that supports window motor operation.
Professional Diagnosis Procedures
Initial Assessment
Visual inspection of window operation forms the foundation of professional diagnosis procedures. Trained technicians observe window movement patterns, speed variations, and mechanical alignment throughout the complete range of motion. This initial assessment often reveals mechanical problems that affect motor performance.
Switch and control testing involves systematic verification of electrical command signals from all window control positions. Professional diagnosis includes testing both local and master window switches to isolate control system problems from motor-specific issues. Proper switch function is essential for accurate motor diagnosis.
Electrical system checks encompass comprehensive evaluation of power supply, ground connections, and circuit integrity throughout the window control system. Voltage measurements at the motor connector provide definitive information about electrical supply adequacy and help identify wiring problems.
Physical examination of door panel components includes inspection of mounting hardware, connector conditions, and visible component damage. Professional technicians look for signs of moisture intrusion, physical damage, or unusual wear patterns that might affect motor operation or longevity.
Environmental assessment considers factors such as climate exposure, usage patterns, and maintenance history that influence motor condition and expected service life. This information helps determine appropriate repair strategies and preventive maintenance recommendations.
Documentation of symptoms and operational history provides valuable diagnostic information that guides testing procedures and repair recommendations. Accurate symptom description often points directly to specific component failures and helps avoid unnecessary diagnostic time and expense.
Electrical Testing
Multimeter voltage testing provides precise measurement of electrical supply conditions at the motor connector. Professional diagnosis requires verification of proper voltage levels under both no-load and operational conditions to identify supply problems or excessive voltage drop in the electrical system.
Current draw measurements reveal motor condition by comparing actual operational current with manufacturer specifications. Excessive current draw indicates mechanical binding or motor deterioration, while insufficient current suggests electrical supply problems or internal motor faults.
Continuity testing of wiring verifies circuit integrity throughout the window control system. This testing identifies open circuits, short circuits, or high-resistance connections that can cause intermittent or complete motor failure. Proper wiring is essential for reliable motor operation.
Switch functionality verification ensures that control commands reach the motor correctly and with proper timing. Professional testing includes verification of switch contact resistance and proper voltage switching under various operational conditions.
Ground circuit testing confirms adequate electrical return paths that are essential for proper motor operation. Poor ground connections can cause erratic operation, reduced performance, or complete motor failure.
Connector inspection includes verification of proper pin engagement, corrosion assessment, and contact resistance measurement. High-quality electrical connections are crucial for reliable motor operation and long-term system durability.
Mechanical Inspection
Window regulator examination determines the mechanical condition of components that work directly with the motor. Regulator binding, wear, or damage can overload the motor and cause premature failure. Professional diagnosis includes complete regulator assessment to ensure proper motor loading.
Motor mounting assessment verifies secure attachment and proper alignment of the motor within the door panel. Loose or damaged mounting can cause noise, vibration, and accelerated wear of both motor and regulator components. Proper mounting is essential for optimal performance.
Lubrication and adjustment checks ensure that mechanical components operate with minimum resistance and proper alignment. Inadequate lubrication or misadjustment can cause excessive motor loading and premature component failure. Regular maintenance prevents many motor problems.
Component wear evaluation includes assessment of gear condition, bearing wear, and mechanical clearances throughout the window system. Professional technicians can often identify developing problems before complete failure occurs, allowing for planned maintenance.
Track and guide inspection reveals mechanical problems that can cause motor overload. Bent tracks, damaged guides, or accumulated debris can create binding conditions that force motors to work beyond design limits.
Foreign object detection involves systematic inspection for debris, broken components, or other materials that might interfere with normal window operation. Even small objects can cause significant operational problems and motor damage if not removed promptly.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Scan tool integration provides access to sophisticated diagnostic information in modern vehicles equipped with computerized window control systems. Professional diagnostic equipment can retrieve fault codes, operational parameters, and system status information that significantly improves diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
Oscilloscope testing enables detailed analysis of motor electrical characteristics during operation. This advanced testing reveals motor condition, electrical supply quality, and operational timing with precision impossible using basic test equipment. Professional facilities often employ oscilloscope testing for complex problems.
Load testing procedures determine motor capacity under controlled conditions to assess remaining service life and operational capability. These tests can identify motors that are approaching failure before complete breakdown occurs, enabling proactive replacement.
Professional assessment criteria incorporate manufacturer specifications, industry standards, and practical experience to determine appropriate repair recommendations. Qualified technicians consider multiple factors including component condition, vehicle age, and cost-effectiveness when recommending repairs.
Specialized tools for window system diagnosis may include motor actuators, regulator alignment fixtures, and electrical load simulators that enable comprehensive system testing under controlled conditions.
Quality assurance procedures ensure that diagnosis is accurate and complete before recommending repairs or replacement. Professional facilities follow systematic diagnostic protocols that minimize errors and ensure appropriate repair recommendations.
Door Window Motor Replacement Process
Safety Preparation
Safety Warning: Electrical automotive work requires proper precautions and professional expertise. Always disconnect the vehicle battery and follow manufacturer safety procedures before beginning any electrical component work. Improper procedures can result in electrical shock, component damage, or personal injury.
Required tools and equipment for motor replacement typically include basic hand tools, electrical test equipment, and specialized automotive trim removal tools. Professional-quality tools ensure safe and efficient component access while minimizing risk of damage to door panel components or electrical systems.
Workspace preparation involves adequate lighting, clean work surfaces, and proper ventilation for safe component handling. Door panel work requires sufficient space to lay out removed components and maintain organization throughout the replacement process.
Personal protective equipment includes safety glasses, work gloves, and appropriate clothing to protect against cuts, electrical hazards, and chemical exposure. Proper safety equipment is essential for preventing injuries during automotive electrical work.
Battery disconnection must be performed properly to prevent electrical system damage and ensure worker safety. Remove the negative battery cable first and secure it away from the battery terminal to prevent accidental reconnection during work.
Component protection involves covering interior surfaces and electronics to prevent damage from debris, tools, or cleaning materials during the replacement process. Professional care during disassembly prevents costly secondary damage.
Removal Procedures
Door panel removal requires systematic disassembly following manufacturer-specified procedures to prevent damage to trim pieces, fasteners, or internal components. Professional technicians follow detailed removal sequences that minimize risk of component breakage and ensure proper reassembly.
Electrical disconnection procedures must be performed carefully to prevent damage to connectors or wiring harnesses. Motor electrical connectors often incorporate locking mechanisms that require proper release procedures to avoid damage during disconnection.
Motor mounting bracket access typically requires removal of multiple fasteners and may involve repositioning of other door panel components. Proper access ensures safe motor removal and prevents damage to surrounding components during the replacement process.
Careful component extraction prevents damage to the motor, door panel, or adjacent components during removal. Window motors are often installed in confined spaces that require specific removal techniques and procedures for safe extraction.
Window position adjustment may be necessary to provide adequate access to motor mounting points. Professional technicians often use specialized tools to hold window glass in safe positions during motor replacement.
Component labeling and organization during disassembly ensures proper reassembly and prevents loss of small parts or fasteners. Professional practices include detailed documentation of component positions and connections for accurate reinstallation.
Installation Guidelines
New motor verification includes functional testing and specification comparison to ensure proper replacement component selection. Quality replacement motors should meet or exceed original equipment specifications for reliable performance and long service life.
Proper mounting and alignment ensures optimal motor performance and prevents premature wear or operational problems. Installation procedures must follow manufacturer torque specifications and alignment requirements for proper system function.
Electrical connection restoration requires careful attention to connector engagement, wire routing, and protection from damage. Proper electrical connections are crucial for reliable motor operation and long-term system durability.
System functionality testing confirms proper operation throughout the complete range of window movement before final reassembly. Professional installation includes comprehensive testing to verify correct operation and identify any remaining problems.
Quality assurance procedures ensure that installation meets professional standards and that all safety requirements are satisfied before returning the vehicle to service. Proper documentation of work performed supports warranty coverage and future service needs.
Component break-in procedures may be recommended for optimal motor performance and longevity. New motors may require initial operating cycles to achieve full performance capability and proper component seating.
Professional Considerations
When to seek professional help includes situations involving complex electrical systems, safety-critical components, or procedures requiring specialized tools and expertise. Electrical automotive work often exceeds DIY capabilities and requires professional knowledge for safe completion.
Warranty considerations affect repair strategies and component selection, particularly for newer vehicles with remaining factory coverage. Professional repair facilities can often provide warranty-compliant repairs that maintain coverage and ensure quality workmanship.
Complex electrical integration in modern vehicles may require programming, calibration, or system initialization procedures that exceed basic replacement requirements. Advanced vehicle systems often require professional expertise for proper installation and programming.
Quality assurance testing confirms proper system operation and identifies any remaining problems before the vehicle is returned to service. Professional facilities typically provide comprehensive testing and documentation of repair work performed.
For comprehensive understanding of related electrical system components, refer to our detailed guides on automotive electrical systems and their interconnections. Proper system integration requires understanding of how window motors interact with other vehicle electrical components.
Preventive Maintenance and Care
Regular Maintenance Practices
Periodic operation testing helps identify developing problems before complete failure occurs. Monthly testing of all windows throughout their full range of motion can reveal early symptoms such as reduced speed, unusual noises, or intermittent operation that indicate developing motor or regulator problems.
Lubrication of window tracks and regulator components reduces operational resistance and extends motor life. Proper lubricants designed for automotive applications help prevent binding and reduce the load on window motors during normal operation. However, over-lubrication can attract debris and cause operational problems.
Electrical connection inspection includes periodic checking of motor connectors, wiring harnesses, and related electrical components for signs of corrosion, loose connections, or damage. Clean, tight electrical connections are essential for reliable motor operation and long service life.
Environmental protection measures help prevent moisture intrusion and corrosion that can cause premature motor failure. Regular inspection and maintenance of door seals, drainage systems, and weather stripping prevents water entry that damages electrical components.
Seasonal maintenance considerations include preparation for extreme weather conditions that can affect window motor operation. Cold weather preparation may include lubrication updates, while hot climate considerations focus on thermal protection and electrical system capacity.
Documentation of maintenance activities helps track component condition and identify patterns that might indicate developing problems. Maintenance records support warranty claims and help service technicians diagnose problems more efficiently.
Extending Motor Life
Proper window operation techniques help prevent unnecessary motor stress and extend component life. Avoid forcing windows against obstructions or operating them rapidly in succession without allowing cooling time between cycles. Patient operation prevents overheating and excessive wear.
Avoiding excessive force during window operation protects both motor and regulator components from damage. If a window encounters resistance, investigate the cause rather than forcing operation that can cause component damage. Ice, debris, or mechanical binding require attention before continued operation.
Climate considerations include understanding how temperature extremes affect window motor operation and taking appropriate precautions. Cold weather can increase operational resistance, while hot conditions can cause electrical components to overheat more readily.
Early problem identification enables proactive maintenance and prevents minor issues from developing into major failures. Attention to subtle changes in window operation can identify problems while they’re still economical to repair rather than waiting for complete failure.
Professional inspection during routine service can identify developing problems and recommend preventive measures that extend motor life and prevent unexpected failures. Regular professional assessment is particularly valuable for high-mileage vehicles.
Understanding the relationship between different vehicle systems helps maintain optimal conditions for window motor operation. Proper electrical system maintenance supports all electrical components including window motors.
Cost Considerations and Planning
Repair vs Replacement Decision
Cost analysis factors include component prices, labor requirements, and expected service life of repair versus replacement options. Quality replacement motors typically offer better long-term value than temporary repairs to severely worn components, particularly when considering labor costs.
Labor considerations vary significantly between different vehicle types and motor accessibility. Some window motor replacements require extensive door panel disassembly that increases labor time and cost compared to more accessible installations. Professional estimates should include all necessary labor operations.
Parts availability and quality affect both immediate repair costs and long-term reliability expectations. Original equipment quality replacement parts typically cost more initially but offer superior reliability and longer service life compared to economy alternatives.
Long-term reliability expectations help evaluate the total cost of ownership for different repair options. Quality repairs performed with proper parts and procedures typically provide years of reliable service, while temporary fixes often require repeated attention and additional costs.
Warranty coverage considerations may influence repair decisions, particularly for newer vehicles with remaining factory coverage or extended warranty protection. Understanding warranty terms helps make cost-effective repair decisions.
Vehicle age and condition influence repair recommendations, as extensive repairs on high-mileage vehicles may not provide adequate return on investment compared to addressing only essential safety and functionality requirements.
Professional Service Options
Dealership versus independent repair facilities offer different advantages in terms of expertise, parts availability, and cost structures. Dealerships typically have specialized knowledge and tools for specific vehicle brands, while independent shops may offer more competitive pricing for routine repairs.
Warranty coverage considerations include understanding what repairs are covered under various warranty types and how different service options affect coverage continuation. Some warranty types require specific repair procedures or authorized service facilities to maintain coverage.
Quality of replacement parts significantly affects repair durability and long-term satisfaction. Professional service facilities can often provide guidance on part selection that balances cost considerations with reliability expectations and performance requirements.
Service documentation importance includes maintaining records that support warranty claims, facilitate future repairs, and provide evidence of proper maintenance. Professional repair facilities typically provide detailed documentation that supports vehicle value and serviceability.
Relationship development with qualified service providers offers advantages in terms of understanding vehicle history, prioritizing service needs, and receiving reliable repair recommendations that consider individual circumstances and requirements.
Cost transparency helps vehicle owners make informed decisions about repair options and service providers. Professional facilities should provide detailed estimates that explain recommended repairs and alternatives with associated costs and benefits.
Conclusion
Door window motor problems require systematic diagnosis and appropriate professional intervention to ensure safe, reliable operation of this essential vehicle system. Understanding the symptoms and underlying causes of motor failure enables vehicle owners to make informed decisions about maintenance and repair timing before minor issues become major safety concerns.
Proper electrical system maintenance and careful attention to early warning signs can significantly extend motor life and prevent unexpected failures that compromise vehicle security and weather protection. Regular inspection and appropriate preventive maintenance represent wise investments in both safety and economy.
The complexity of modern automotive electrical systems often requires professional expertise for accurate diagnosis and proper repair procedures. Safety considerations and the potential for electrical system damage make professional consultation advisable for all but the most basic maintenance tasks.
When motor problems occur, prompt attention prevents secondary damage and ensures continued vehicle safety and functionality. Quality repairs performed with appropriate parts and procedures typically provide years of reliable service and maintain vehicle value.
Remember that window motor problems affect both convenience and safety, making timely repair a priority rather than an option. Proper diagnosis, quality parts, and professional installation ensure optimal performance and longevity from this essential vehicle system.
For additional information about automotive electrical systems and professional repair resources, contact qualified service professionals who can provide guidance specific to your vehicle and circumstances. Professional consultation ensures appropriate repair strategies and maintains vehicle safety and reliability standards.
