Disclaimer: This information is provided for reference only. All repair procedures should be implemented at your own risk and responsibility. Safety-first approach is mandatory. For complex procedures, professional consultation is strongly recommended.
Imagine pressing your clutch pedal and hearing an unusual squealing or grinding noise coming from under the hood. This scenario is all too common and often points to a failing clutch release bearing, one of the most critical yet frequently overlooked components in your vehicle’s clutch system. When this small but vital part begins to fail, it can lead to complete clutch system breakdown and expensive repairs.
Understanding your clutch release bearing and recognizing early warning signs can save you significant time, money, and frustration. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about clutch release bearings, from basic function to advanced diagnostic techniques, helping you make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
Whether you’re experiencing strange noises during clutch operation, considering a DIY repair, or simply want to better understand your vehicle’s drivetrain system, this article provides the technical knowledge and practical guidance you need. We’ll cover symptom identification, diagnostic procedures, replacement considerations, and when to seek professional help.
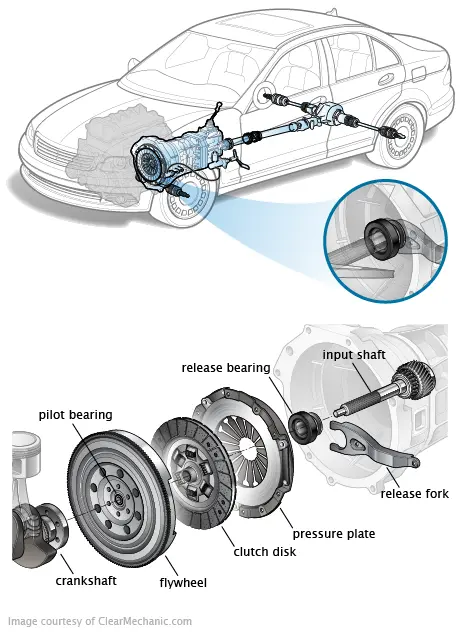
What is a Clutch Release Bearing?
The clutch release bearing, also known as a throwout bearing, is a critical component that enables smooth clutch operation by transferring force from the clutch pedal to the pressure plate. Located between the clutch fork and the pressure plate fingers inside the transmission bell housing, this bearing serves as the crucial link that allows drivers to engage and disengage the clutch smoothly.
Primary Function and Location
The release bearing’s primary function is to transfer clutch pedal force to the pressure plate while accommodating the rotational differences between stationary and moving components. When you press the clutch pedal, the release bearing moves forward along the transmission input shaft, contacting the pressure plate’s diaphragm spring fingers and pulling them back to disengage the clutch disc from the flywheel.
This component operates in one of the most demanding environments in your vehicle, dealing with high rotational speeds, significant pressure loads, and elevated temperatures. The bearing must maintain smooth operation while pressed against rotating pressure plate fingers, making its design and construction critical to overall clutch system performance.
Component Breakdown
A typical clutch release bearing assembly consists of several key elements working together:
Bearing Assembly: The core component features either ball bearings or roller bearings housed within a precision-machined housing. These bearings handle the rotational loads while maintaining smooth operation under pressure.
Release Collar: This component interfaces directly with the clutch fork, providing the mechanical connection that transfers pedal force to the bearing assembly. The collar design varies between mechanical and hydraulic clutch systems.
Contact Surface: The front face of the bearing contacts the pressure plate’s diaphragm spring fingers. This surface must be precisely manufactured to ensure even pressure distribution and minimize wear.
Types of Release Bearings
Modern vehicles employ different release bearing designs depending on the clutch system configuration:
Mechanical Systems use traditional release bearings that operate through cable or linkage connections. These systems require periodic adjustment as clutch components wear, and the release bearing typically features a simple but robust design optimized for direct mechanical actuation.
Hydraulic Systems often incorporate more sophisticated release bearing designs that integrate with slave cylinder operation. Some modern systems use self-adjusting hydraulic release bearings that automatically compensate for clutch wear, reducing maintenance requirements.
Material Variations include steel housings for durability, composite materials for weight reduction, and specialized ceramic components for high-performance applications. The choice depends on vehicle requirements, operating conditions, and performance expectations.
Understanding the relationship between your release bearing and other clutch system components is essential for proper diagnosis and maintenance. The bearing works in close coordination with the clutch disc, pressure plate, and flywheel to provide smooth power transfer and reliable operation.
How the Clutch Release Bearing Works
The clutch release bearing operates through a precise sequence of mechanical actions that enable smooth clutch engagement and disengagement. Understanding this operating cycle is crucial for diagnosing problems and appreciating the component’s critical role in your vehicle’s drivetrain system.
Operating Cycle Explanation
The release bearing’s operation begins when you press the clutch pedal, initiating a chain reaction throughout the clutch system:
- Clutch Pedal Pressed: Driver input creates initial force that travels through either cable or hydraulic systems to activate the clutch fork mechanism.
- Force Transmission: The clutch fork pivots on its mounting point, transferring and amplifying the pedal force to push the release bearing forward along the transmission input shaft.
- Bearing Engagement: The release bearing contacts the pressure plate’s diaphragm spring fingers, applying concentrated force to overcome spring pressure and initiate pressure plate movement.
- Pressure Plate Disengagement: As the diaphragm spring fingers are pulled back, the pressure plate moves away from the clutch disc, reducing clamping force between the disc and flywheel.
- Clutch Separation: With pressure removed, the clutch disc separates from the flywheel, interrupting power transfer and allowing gear changes or vehicle stopping without engine stalling.
This entire sequence must occur smoothly and repeatedly throughout the vehicle’s operational life, placing significant demands on the release bearing’s design and construction.
Mechanical vs. Hydraulic Systems
Cable-Operated Systems provide direct mechanical linkage between the clutch pedal and release bearing. These systems offer immediate response and simple troubleshooting but require regular adjustment as components wear. The release bearing in cable systems typically experiences more variable loading due to direct mechanical connection.
Hydraulic Systems use clutch master cylinder and slave cylinder components to transfer pedal force through pressurized brake fluid. This design provides consistent pedal feel and automatic load distribution but requires additional maintenance for hydraulic components. Modern hydraulic systems often incorporate release bearings that remain in constant contact with pressure plate fingers, reducing engagement shock.
Self-Adjusting Mechanisms in contemporary vehicles automatically compensate for clutch wear, maintaining proper pedal feel and release bearing positioning throughout the clutch’s service life. These systems reduce maintenance requirements but add complexity to diagnosis and repair procedures.
Load Distribution and Stress Points
The release bearing must handle significant mechanical stresses during operation. Contact pressure between the bearing and pressure plate fingers can exceed 1,000 pounds of force, concentrated in a relatively small contact area. This pressure varies with clutch design, vehicle weight, and driving conditions.
Rotational speeds present another challenge, as the bearing operates while the transmission input shaft spins at engine RPM. Modern bearings must maintain smooth operation at speeds exceeding 6,000 RPM while under load, requiring precise manufacturing tolerances and high-quality lubrication.
Heat generation occurs due to friction between moving surfaces and pressure plate contact. Effective heat dissipation is crucial for bearing longevity, making proper lubrication and ventilation essential for reliable operation.
Integration with Clutch Components
The release bearing’s effectiveness depends on proper integration with all clutch system components. Pressure plate interface requires precise alignment and appropriate contact pressure to ensure even wear and smooth operation. Improper installation or worn components can cause premature bearing failure.
Clutch fork relationship affects force multiplication and bearing travel distance. Proper fork pivot points and leverage ratios ensure adequate force transmission without excessive bearing stress. Worn fork components can cause erratic bearing operation and accelerated wear.
Understanding how your release bearing works with related components like the clutch pressure plate and clutch pilot bearing helps in comprehensive system diagnosis and maintenance planning.
Common Clutch Release Bearing Problems
Clutch release bearing failures manifest through several distinct failure modes, each presenting specific symptoms that can help with accurate diagnosis. Understanding these failure patterns enables early intervention and prevents more extensive clutch system damage.
Primary Failure Modes
Bearing Wear represents the most common failure mode, occurring when the internal ball bearings or roller bearings deteriorate due to normal use, contamination, or inadequate lubrication. As bearing surfaces wear, internal clearances increase, leading to noise, vibration, and eventual complete failure. This wear pattern typically develops gradually, providing warning signs before complete breakdown.
Seal Failure allows grease to escape from the bearing assembly while permitting dirt, moisture, and debris to enter. Once contamination occurs, bearing wear accelerates rapidly, often causing sudden failure. Seal deterioration is particularly common in high-mileage vehicles or those operated in harsh environmental conditions.
Housing Damage can result from excessive force, misalignment, or impact during installation. Cracked or deformed housings cannot properly support the bearing assembly, leading to irregular operation and premature wear. This type of damage often occurs during clutch replacement if proper installation procedures aren’t followed.
Surface Wear affects the bearing’s contact surface where it interfaces with the pressure plate fingers. Excessive wear creates uneven contact pressure, causing noise, vibration, and reduced clutch performance. This wear pattern often indicates problems with pressure plate alignment or excessive operating temperatures.
Noise-Related Symptoms
Squealing When Clutch Pressed represents one of the most recognizable release bearing symptoms. This high-pitched noise typically occurs only when the clutch pedal is depressed and the bearing contacts the pressure plate fingers. The squealing usually indicates dry bearing surfaces or initial bearing wear, serving as an early warning sign.
Grinding Sounds suggest more advanced bearing deterioration, often indicating metal-on-metal contact between worn bearing components. This symptom requires immediate attention, as continued operation can cause severe damage to the pressure plate and other clutch components. Grinding noises may be accompanied by pedal vibration or irregular clutch operation.
Chirping or Chattering often manifests as intermittent noise during clutch operation, particularly during initial engagement or release. This symptom can indicate uneven bearing wear, contamination, or problems with the clutch fork mechanism. The irregular nature of this noise pattern makes it important to document when and under what conditions it occurs.
Noise Timing provides crucial diagnostic information. Sounds that occur only when the clutch pedal is pressed typically indicate release bearing problems, while noises present when the pedal is released often point to other clutch components like the clutch disc or pilot bearing.
Performance Issues
Hard Clutch Pedal can result from binding or damaged release bearing components that increase the force required for clutch operation. This symptom often develops gradually and may be accompanied by changes in pedal travel or engagement point. Increased pedal effort can also indicate problems with the clutch cable or hydraulic system components.
Clutch Slipping may occur if bearing problems prevent complete pressure plate engagement, allowing the clutch disc to slip against the flywheel under load. While slipping can have multiple causes, release bearing issues should be considered when other symptoms are present.
Engagement Problems manifest as difficulty shifting gears, particularly when moving from neutral to first gear or reverse. If the release bearing cannot fully disengage the clutch, gear changes become difficult or impossible, especially from a stopped position.
Pedal Feel Changes include vibration, irregular resistance, or changes in the engagement point. These symptoms often indicate bearing wear or damage that affects smooth clutch operation. Documenting these changes helps technicians identify the root cause during diagnosis.
Progressive Failure Patterns
Early Stage release bearing problems typically present as occasional noise during specific operating conditions, such as cold weather or initial startup. These symptoms may be intermittent and easily overlooked but represent important early warning signs.
Intermediate Stage failure involves consistent noise and noticeable performance changes during normal operation. Symptoms become more pronounced and frequent, indicating the need for prompt attention to prevent further damage.
Advanced Stage problems include severe noise, significant performance loss, and potential damage to other clutch components. At this point, continued operation risks expensive secondary damage to the pressure plate, clutch disc, or flywheel surfaces.
Understanding these failure patterns helps determine urgency and guides repair planning. For comprehensive clutch system evaluation, consider reviewing our guide on diagnosing clutch problems to understand how release bearing issues fit into the broader context of clutch system maintenance.
Diagnosing Clutch Release Bearing Issues
Accurate diagnosis of release bearing problems requires systematic evaluation of symptoms, operating conditions, and physical component inspection. Proper diagnostic techniques help distinguish release bearing issues from other clutch system problems and guide appropriate repair decisions.
Initial Assessment Techniques
Sound Diagnosis provides the most immediate diagnostic information for release bearing evaluation. Begin by identifying the specific conditions when noise occurs: engine running versus off, clutch engaged versus disengaged, and any relationship to engine RPM or vehicle speed.
To isolate bearing noise from other clutch components, start the engine and listen for sounds with the clutch pedal released. If noise is present, it typically indicates problems with the pilot bearing or transmission input shaft bearings rather than the release bearing. Press the clutch pedal halfway and listen for changes in noise character or intensity, which often reveals release bearing contact issues.
Noise location techniques involve careful listening from different positions around the vehicle. Release bearing noise typically originates from the transmission bell housing area and may be more pronounced from underneath the vehicle or through the engine compartment. Use a mechanic’s stethoscope or similar listening device to pinpoint the exact noise source.
Operating condition testing should include evaluation at idle, various RPM levels, and during actual driving conditions. Note any changes in noise character with engine temperature, as some bearing problems become more pronounced when components reach operating temperature.
Physical Inspection Methods
Clutch Pedal Feel Assessment reveals important information about release bearing condition and overall clutch system health. Normal pedal operation should feel smooth and consistent throughout the pedal travel, with a distinct engagement point and appropriate resistance.
Irregular pedal feel, including vibration, binding, or unusual resistance patterns, often indicates bearing wear or damage. Document the pedal free play measurement and compare it to manufacturer specifications, as excessive free play can indicate bearing wear or adjustment problems.
Fluid Level Checks are essential for hydraulic clutch systems, as low fluid levels can cause erratic bearing operation and accelerated wear. Inspect the clutch fluid reservoir and check for signs of leakage around the master cylinder, slave cylinder, and hydraulic lines. Contaminated or discolored fluid may indicate internal seal problems affecting bearing operation.
Visual Component Assessment requires inspection of accessible clutch system components, including the clutch fork, bell housing, and any visible portions of the release bearing assembly. Look for signs of grease leakage, metal particles, or component misalignment that could indicate bearing problems.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
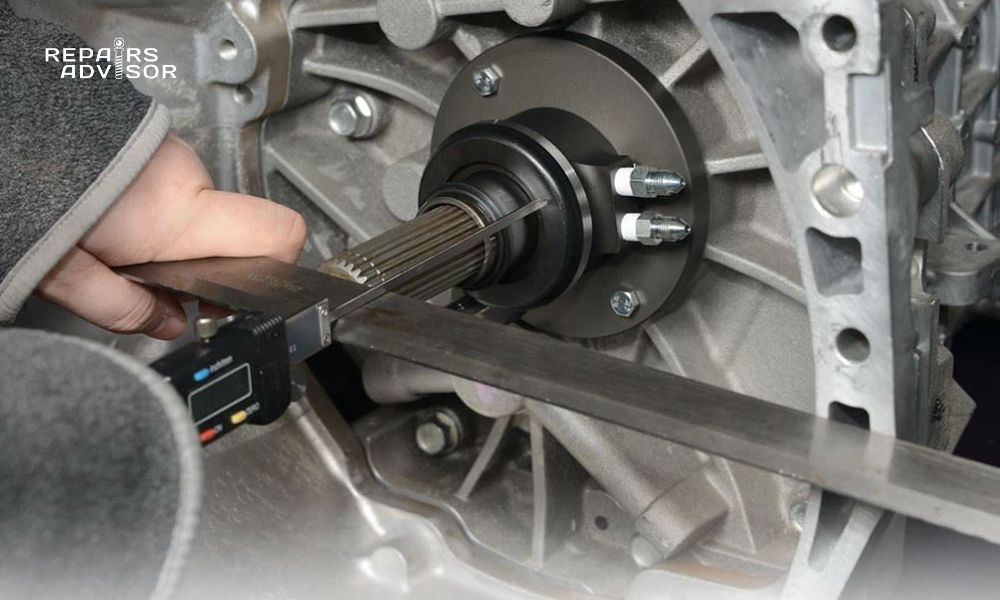
Professional Inspection Techniques often require partial disassembly to access internal components. This typically involves removing the transmission to expose the clutch assembly and release bearing for direct inspection. Professional diagnosis includes measurement of bearing play, assessment of contact surface wear, and evaluation of related component condition.
Component Measurement involves checking bearing assembly dimensions, clutch fork alignment, and pressure plate finger condition. Specialized tools may be required to measure bearing clearances and assess the condition of internal bearing components.
System Integration Testing evaluates the relationship between the release bearing and other clutch components, including pressure plate alignment, clutch disc condition, and flywheel surface quality. This comprehensive approach ensures that bearing replacement addresses all contributing factors to prevent premature failure.
Diagnostic Tool Requirements
Basic Tools for initial diagnosis include standard hand tools for visual inspection, a stethoscope or similar listening device for sound diagnosis, and measurement tools for pedal free play assessment. These tools enable most preliminary diagnostic procedures without major disassembly.
Specialized Equipment may include bearing pullers for safe removal, alignment tools for proper installation, and hydraulic pressure testers for system evaluation. Professional shops typically have access to more sophisticated diagnostic equipment for comprehensive clutch system analysis.
Safety Equipment is essential for any diagnostic procedure involving vehicle lifting or component removal. Proper jack stands, transmission support tools, and personal protective equipment ensure safe working conditions during diagnosis and repair.
Differential Diagnosis
Release Bearing vs. Pilot Bearing differentiation is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Release bearing problems typically manifest when the clutch pedal is pressed, while pilot bearing issues often cause noise when the pedal is released and the transmission is in gear.
Pressure Plate Issues can sometimes mimic release bearing problems, particularly when diaphragm spring fingers are worn or damaged. Pressure plate problems often cause irregular engagement characteristics and may be accompanied by clutch slipping or grabbing.
Clutch Disc Problems typically affect engagement smoothness and may cause slipping or chattering during operation. Understanding the differences between these symptoms helps focus diagnostic efforts and ensures accurate problem identification.
Proper diagnosis forms the foundation for effective repair planning and helps determine whether professional service is necessary for complex issues requiring specialized tools or expertise.
Clutch Release Bearing Replacement Process
SAFETY WARNING: Clutch release bearing replacement requires transmission removal, specialized tools, and precise alignment procedures. This repair involves heavy components weighing 100+ pounds and requires proper lifting equipment. Professional installation is strongly recommended for safety and proper operation. The following information is provided for educational purposes and should not be attempted without appropriate experience, tools, and safety equipment.
Pre-Replacement Assessment
Component Evaluation begins with thorough assessment of the failed bearing and related clutch components. Examine the condition of the clutch disc, pressure plate, and flywheel surface to determine if additional components require replacement. Since transmission removal is required for bearing access, this presents an ideal opportunity for complete clutch system service.
Related Component Inspection should include evaluation of the clutch fork, pilot bearing, and hydraulic system components (if equipped). Worn or damaged related components can cause premature failure of the new release bearing, making comprehensive assessment essential for long-term reliability.
System Integration Planning involves deciding between bearing-only replacement and complete clutch service. Given the labor involved in transmission removal, many technicians recommend replacing the entire clutch assembly when the release bearing fails, particularly in high-mileage vehicles.
Tool and Equipment Requirements
Basic Tools include comprehensive socket sets, combination wrenches, pry bars, and standard hand tools for component removal and installation. Quality tools are essential for safe and efficient work, particularly when dealing with tight fastener access and heavy component manipulation.
Specialized Equipment requirements include a transmission jack capable of supporting the transmission weight safely, engine support fixtures to prevent engine movement during transmission removal, and bearing installation tools for proper bearing positioning and alignment.
Safety Equipment must include appropriate jack stands rated for the vehicle weight, wheel chocks to prevent vehicle movement, and personal protective equipment including safety glasses and gloves. Never attempt this repair without proper safety equipment and adequate workspace.
Step-by-Step Replacement Overview
Preparation Phase involves positioning the vehicle on level ground, engaging the parking brake, and disconnecting the battery to prevent accidental electrical activation. Remove the transmission access covers and drain transmission fluid to prevent spillage during removal.
Component Access requires systematic removal of components blocking transmission access, including the driveshaft, exhaust system components, and electrical connections. Document wire routing and connector positions to ensure proper reassembly.
Removal Sequence follows manufacturer-specified procedures for transmission disconnection and removal. Support the transmission weight with appropriate equipment before removing mounting bolts, and ensure adequate clearance for safe transmission lowering.
- Transmission Removal: Disconnect the driveshaft, shift linkage, electrical connections, and hydraulic lines. Support the transmission with a transmission jack and remove mounting bolts following the specified sequence to prevent binding or damage.
- Clutch Component Access: With the transmission removed, the clutch assembly becomes accessible for component removal. Mark the pressure plate position relative to the flywheel before removal to maintain balance during reassembly.
- Release Bearing Removal: Disconnect the clutch fork from the bearing assembly and remove the bearing from its guide sleeve. Inspect the bearing guide surfaces for wear or damage that could affect new bearing operation.
- Component Inspection: Evaluate all accessible components for wear, damage, or contamination. This inspection guides decisions about additional component replacement and helps identify contributing factors to bearing failure.
Installation Process
New Bearing Preparation includes verification of correct part numbers and application of appropriate lubrication to bearing contact points. Follow manufacturer specifications for lubricant type and quantity, as improper lubrication can cause premature failure.
Bearing Installation requires careful positioning and alignment to ensure proper contact with pressure plate fingers and clutch fork mechanism. Use appropriate installation tools to prevent bearing damage during installation.
Clutch Component Reassembly follows reverse removal procedures with attention to proper torque specifications and component alignment. Install the clutch disc with appropriate alignment tools to ensure concentricity with the flywheel and pressure plate.
Transmission Reinstallation requires careful alignment of the transmission input shaft with the clutch disc splines. Use pilot alignment tools to prevent clutch disc damage during transmission installation.
Critical Installation Points
Bearing Alignment must ensure proper contact between the bearing and pressure plate fingers without binding or excessive pressure. Incorrect alignment can cause immediate bearing failure or poor clutch operation.
Lubrication Requirements specify appropriate grease types and application points for optimal bearing performance. Use high-temperature bearing grease designed for clutch applications, avoiding over-lubrication that can attract contamination.
Torque Specifications must be followed precisely for all fasteners, particularly pressure plate bolts that require specific torque sequences to maintain proper pressure distribution. Incorrect torque can cause pressure plate distortion and premature component failure.
System Bleeding applies to hydraulic clutch systems and requires proper air removal procedures to ensure consistent clutch operation. Follow manufacturer bleeding procedures to prevent air pockets that could affect bearing operation.
Post-Installation Procedures
Initial Adjustment includes setting proper clutch pedal free play and verifying correct engagement point. These adjustments ensure optimal bearing operation and prevent premature wear due to constant bearing contact.
System Testing should include evaluation of clutch engagement, disengagement, and noise levels during initial operation. Perform testing at idle and various RPM levels to verify proper bearing operation under different conditions.
Break-in Period recommendations typically include avoiding heavy loads and aggressive clutch operation for the first few hundred miles to allow proper component seating and bedding. Follow manufacturer guidelines for new clutch break-in procedures.
For detailed information about related components that may require attention during bearing replacement, review our articles on clutch safety switch operation and automatic transmission fluid maintenance for comprehensive drivetrain care.
Prevention and Maintenance
Effective clutch release bearing maintenance focuses on preventing premature failure through proper operating practices, regular inspection, and early intervention when problems develop. Understanding maintenance requirements helps maximize bearing life and avoid unexpected failures.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Regular Inspection Schedule should include monthly visual checks of accessible clutch system components, quarterly assessment of clutch pedal operation and feel, and annual professional evaluation for high-mileage vehicles or those operated under severe conditions.
During visual inspections, look for signs of fluid leakage around hydraulic components, unusual wear patterns on accessible parts, and any changes in component positioning or alignment. Document any changes from previous inspections to track developing problems.
Performance Monitoring involves paying attention to clutch operation characteristics during normal driving. Note any changes in pedal feel, engagement point, or operating noise that could indicate developing bearing problems. Early recognition of these changes enables intervention before major failure occurs.
Fluid Maintenance for hydraulic clutch systems includes regular fluid level checks, periodic fluid replacement according to manufacturer schedules, and immediate attention to any signs of leakage or contamination. Clean, properly maintained hydraulic fluid helps ensure consistent bearing operation and prevents contamination-related failures.
Operating Practices
Proper Clutch Technique significantly affects release bearing life. Avoid “riding the clutch” by keeping your foot off the clutch pedal except when shifting or stopping. Constant pedal pressure keeps the bearing in contact with pressure plate fingers, causing unnecessary wear and heat generation.
Complete engagement and disengagement during gear changes reduces bearing stress and wear. Partial clutch operation creates slipping conditions that generate heat and accelerate component deterioration. Take time to fully depress and release the clutch pedal during gear changes.
Load Management involves avoiding excessive loads that stress clutch components beyond their design limits. Heavy towing, aggressive launches, or sustained high-load operation can overstress the release bearing and other clutch components, leading to premature failure.
Environmental Considerations include protecting clutch components from moisture, dirt, and road salt that can accelerate corrosion and contamination. Regular undercarriage cleaning helps remove corrosive materials, while proper storage practices protect vehicles during extended non-use periods.
Early Warning Recognition
Sound Changes often provide the first indication of developing release bearing problems. Learn to recognize normal clutch system sounds during operation, and investigate any new or changing noises promptly. Early intervention based on sound changes can prevent catastrophic failure and secondary damage.
Performance Degradation typically develops gradually, making it important to stay attuned to subtle changes in clutch operation. Document any changes in pedal feel, engagement characteristics, or operating effort to help identify trends that indicate developing problems.
System Monitoring includes regular assessment of clutch adjustment, fluid levels, and component condition. Maintain service records to track maintenance intervals and identify patterns that might indicate accelerated wear or developing problems.
Maintenance Integration
Scheduled Service should incorporate release bearing inspection into routine maintenance procedures. During oil changes or other regular service, take time to assess clutch operation and look for signs of developing problems.
Component Replacement Timing involves coordinating bearing replacement with other clutch service to minimize labor costs and downtime. Since transmission removal is required for bearing access, consider replacing related components that are approaching their service limits.
System Upgrades may include improved bearing designs, enhanced lubrication systems, or upgraded clutch components that offer better durability or performance. Consult with qualified technicians about upgrade options during major service intervals.
Proper maintenance practices help ensure reliable clutch operation and can significantly extend release bearing life. For comprehensive clutch system care, consider reviewing maintenance requirements for other critical drivetrain components that work together to provide smooth power transfer and reliable operation.
Cost Considerations and Professional vs. DIY
Release bearing replacement involves significant cost considerations due to the labor-intensive nature of transmission removal and the complexity of clutch system service. Understanding these costs helps make informed decisions about repair approaches and timing.
Cost Analysis Framework
Parts Costs for release bearings typically range from budget aftermarket options to premium OEM components, with prices varying based on vehicle application and bearing design. While the bearing itself may represent a relatively small portion of total repair costs, the labor required for installation makes component quality an important consideration.
Consider that bearing replacement provides an opportunity for complete clutch service, potentially including clutch disc, pressure plate, pilot bearing, and flywheel refinishing. While this increases parts costs, it maximizes value from the labor investment and helps prevent future failures.
Tool Requirements can represent a significant one-time investment for DIY repairs. Transmission jacks, engine support equipment, and specialized clutch tools may cost more than professional service for occasional use. However, these tools retain value for future repairs and other projects.
Professional tool rental options may provide cost-effective access to specialized equipment for occasional use. Evaluate rental costs against purchase prices when planning DIY repairs, considering storage requirements and future use potential.
Labor Considerations
Professional Installation typically requires 4-8 hours of labor depending on vehicle complexity and additional services performed. Shop labor rates vary significantly by location and facility type, making it important to obtain detailed estimates before committing to repairs.
Quality professional service includes proper diagnostic procedures, appropriate tool usage, warranty coverage on parts and labor, and expertise in handling complex installation procedures. These benefits often justify professional service costs, particularly for critical safety components.
DIY Time Investment requires realistic assessment of project complexity and personal skill level. Transmission removal and installation demands physical capability, appropriate workspace, and patience for methodical procedures. Plan for significantly more time than professional completion estimates.
Complexity Assessment should consider factors including vehicle access, transmission type, hydraulic system requirements, and special tool needs. Some vehicles present particular challenges that favor professional service even for experienced home mechanics.
Decision Factors
DIY Suitability Assessment begins with honest evaluation of mechanical experience, particularly with transmission and clutch work. This repair requires precision, safety awareness, and problem-solving skills for unexpected complications.
Tool Access evaluation should include assessment of workspace requirements, lifting capability, and specialized tool availability. Consider safety equipment needs and workspace limitations that might favor professional service.
Safety Considerations represent the most important decision factor, as improper procedures can result in serious injury from heavy components, vehicle instability, or component failure. Professional service provides trained technicians, appropriate equipment, and insurance coverage for complex procedures.
Value Optimization Strategies
Bulk Replacement during bearing service maximizes value from labor investment. Consider replacing the complete clutch assembly, pilot bearing, and related components during transmission removal to prevent future failures and additional labor costs.
Quality Considerations favor OEM or high-quality aftermarket components for critical clutch system parts. While premium components cost more initially, they typically provide better reliability and longer service life, reducing total ownership costs.
Service Timing coordination with other maintenance needs can reduce overall costs. Schedule bearing replacement with other major services requiring similar access or downtime to maximize efficiency and value.
Professional Service Benefits
Warranty Coverage typically includes parts and labor guarantees that protect against premature failure or installation problems. Professional warranties provide valuable protection for expensive repairs and demonstrate service provider confidence in their work.
Diagnostic Expertise helps ensure accurate problem identification and appropriate repair scope. Professional technicians can identify contributing factors and recommend additional services that prevent premature failure of new components.
Specialized Tools access enables efficient, safe completion of complex procedures. Professional shops invest in appropriate equipment for quality results and worker safety, benefits that are difficult to replicate in home garage environments.
Time Efficiency allows faster project completion with experienced technicians who understand efficient procedures and common complications. Professional efficiency minimizes vehicle downtime and reduces inconvenience.
For additional guidance on related maintenance decisions, consider reviewing information about vehicle care tips and tools and equipment selection for comprehensive vehicle maintenance planning.
When to Seek Professional Help
Certain symptoms and conditions require immediate professional attention to prevent safety hazards, avoid extensive damage, or address issues beyond typical DIY capabilities. Recognizing these situations helps ensure appropriate response and optimal repair outcomes.
Immediate Professional Consultation Indicators
Safety Concerns should trigger immediate professional evaluation when clutch operation becomes unreliable or fails completely. If the clutch cannot disengage properly, vehicle operation becomes dangerous due to inability to stop the engine without stalling or difficulty shifting gears in traffic situations.
Complete clutch system failure requires professional diagnosis to determine the root cause and appropriate repair scope. Attempting to drive with clutch problems can cause secondary damage to transmission components, flywheel surfaces, or other expensive parts.
Complex Symptoms involving multiple system problems often require professional diagnostic expertise to identify root causes and determine appropriate repair priorities. When release bearing problems occur alongside other clutch, transmission, or engine symptoms, professional evaluation helps ensure comprehensive problem resolution.
Tool Limitations become apparent when specialized equipment is required for safe, effective repairs. Professional shops have access to transmission jacks, alignment tools, hydraulic pressure testers, and other specialized equipment that enables safe, efficient completion of complex procedures.
Experience Gaps should be honestly assessed when considering DIY repairs. Clutch system work requires specific knowledge about component relationships, adjustment procedures, and safety considerations that come from training and experience.
Diagnostic Services
Professional Assessment provides comprehensive clutch system evaluation using specialized knowledge and equipment. Professional technicians can identify subtle problems that might be missed during basic DIY diagnosis, helping ensure complete problem resolution.
Specialized Testing capabilities include hydraulic pressure testing, component measurement with precision tools, and systematic evaluation of clutch system integration. These diagnostic capabilities help identify contributing factors and prevent premature failure of replacement components.
Repair Recommendations from qualified professionals provide expert guidance on repair scope, component selection, and timing considerations. Professional recommendations help optimize repair value and prevent unnecessary work or component replacement.
Service Provider Selection
Qualification Verification should include assessment of technician certifications, particularly ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification in relevant specialties. Look for shops with experience in your vehicle type and clutch system configuration.
Warranty Considerations vary significantly between service providers, with some offering comprehensive parts and labor warranties while others provide minimal coverage. Evaluate warranty terms carefully, particularly for expensive repairs involving multiple components.
Cost Transparency requires detailed estimates that clearly identify labor charges, parts costs, and any additional services recommended. Reputable shops provide written estimates and explain repair necessity before beginning work.
Emergency Situations
Complete Clutch Failure requires immediate professional attention to prevent vehicle stranding and ensure safe operation. If clutch operation fails completely, avoid driving and arrange for professional towing to prevent additional damage.
Safety-Related Issues including pedal binding, unexpected engagement, or loss of clutch control require immediate professional evaluation. These conditions present serious safety hazards that require expert diagnosis and repair.
Roadside Assistance provides professional evaluation and initial assessment when clutch problems occur away from home. Professional towing and diagnostic services help ensure safe vehicle handling and appropriate repair facility selection.
Understanding when to seek professional help protects both safety and financial interests by ensuring appropriate response to complex problems. Professional service provides the expertise, equipment, and warranty coverage necessary for reliable repair of critical vehicle systems.
For comprehensive vehicle maintenance support and technical documentation, Repairs Advisor provides access to detailed service manuals and technical resources. If you need specific guidance for your vehicle, contact our support team at [email protected] or visit our contact page for assistance.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The clutch release bearing plays a critical role in your vehicle’s drivetrain operation, serving as the essential link between clutch pedal input and pressure plate control. Understanding this component’s function, recognizing failure symptoms, and knowing when to seek professional help can save significant time, money, and frustration while ensuring safe vehicle operation.
Summary of Critical Points
Component Importance cannot be overstated, as the release bearing enables all clutch operations from gear changes to vehicle stops. When this bearing fails, it affects the entire clutch system and can lead to complete drivetrain dysfunction. Early recognition of problems through sound identification and performance monitoring provides the best opportunity for cost-effective repairs.
Failure Recognition typically begins with unusual noises during clutch operation, particularly squealing or grinding sounds when the clutch pedal is pressed. Progressive symptoms include changes in pedal feel, increased operating effort, and difficulty with gear engagement. Understanding these warning signs enables prompt attention before catastrophic failure occurs.
Maintenance Value through proper operating practices, regular inspection, and early intervention provides the best protection against premature bearing failure. Simple practices like avoiding clutch riding, maintaining proper pedal technique, and monitoring system performance can significantly extend bearing life and prevent expensive repairs.
Decision Support Framework
Assessment Tools provided in this guide help evaluate symptoms, determine problem severity, and guide repair decisions. Systematic diagnostic approaches distinguish release bearing problems from other clutch system issues, ensuring appropriate repair scope and preventing unnecessary work.
Repair Decisions should balance safety considerations, cost factors, and long-term reliability goals. While DIY repairs may be appropriate for experienced mechanics with proper tools, the complexity and safety requirements of transmission removal often favor professional service.
Quality Focus in parts selection and installation procedures ensures reliable repairs and optimal component life. Using quality replacement parts and following proper installation procedures provides the best value from repair investments.
Final Recommendations
Safety Priority must guide all repair decisions, particularly for complex procedures involving heavy components and vehicle lifting. Professional consultation provides the expertise, equipment, and safety protocols necessary for reliable clutch system repairs.
Preventive Approach through regular maintenance, proper operating practices, and early intervention offers the best protection against expensive failures. Monitoring clutch system performance and addressing problems promptly prevents secondary damage and reduces total repair costs.
Resource Utilization includes access to technical manuals, professional guidance, and specialized tools that enable proper diagnosis and repair. Whether pursuing DIY repairs or professional service, having access to accurate technical information ensures optimal results.
The clutch release bearing may be a small component, but its proper operation is essential for safe, reliable vehicle performance. By understanding its function, recognizing problems early, and making informed repair decisions, you can maintain optimal clutch system performance and avoid costly failures.
Remember that clutch system repairs affect vehicle safety and reliability. When in doubt, consult with qualified professionals who have the experience, tools, and expertise to ensure proper diagnosis and repair. The investment in professional service often pays dividends in reliability, safety, and long-term cost savings.
For technical support and access to comprehensive repair manuals specific to your vehicle, Repairs Advisor provides the resources and expertise needed for successful clutch system maintenance and repair.
